Impact of electro-acupuncture on EAAT2 and NMDAR-2B expression in goats with visceral hypersensitivity
- PMID: 39717594
- PMCID: PMC11665384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40700
Impact of electro-acupuncture on EAAT2 and NMDAR-2B expression in goats with visceral hypersensitivity
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluates the effect of electro-acupuncture (EA) on visceral hypersensitivity (VH) and the expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-2B (NMDAR-2B) and glutamate transporter EAAT2 in goats.
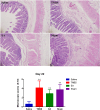
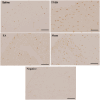
Methods: Twenty-four goats were divided into four groups: saline, 2, 4, 6-Trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS), TNBS + EA, and sham EA. EA was administered at Zusanli (ST36) with 60 Hz and 1-3 mA on specified days. Electromyography (EMG) recorded visceromotor response to colorectal distention (CRD). Spinal cords were collected for immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and RT-PCR. The ileum was examined histologically.
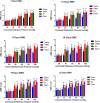
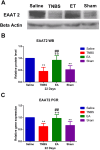
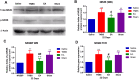
Results: The repeated EA administration significantly attenuated VH (P < 0.05) in TNBS-treated goats without similar effects in the sham group. NMDAR-2B expression increased (P < 0.01), and EAAT2 expression decreased (P < 0.01) in the TNBS group compared to saline. EA increased the EAAT2 and decreased the NMDAR-2B expression (P < 0.01) compared to TNBS, with no change in the sham-EA group.
Conclusion: EA may alleviate VH by upregulating EAAT2 and downregulating NMDAR-2B in the spinal cord of TNBS-treated goats, indicating its potential for treating chronic visceral pain in gastrointestinal disorders.
Keywords: Electro-acupuncture; Glutamate transporter EAAT2; Goat; Ileitis; Inflammatory bowel disease; NMDAR-2B; TNBS; Visceral hypersensitivity.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture relieves visceral hypersensitivity through modulation of the endogenous cannabinoid system.Acupunct Med. 2023 Aug;41(4):224-234. doi: 10.1177/09645284221107699. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Acupunct Med. 2023. PMID: 35957508
-
Electroacupuncture intervention of visceral hypersensitivity is involved in PAR-2-activation and CGRP-release in the spinal cord.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 7;10(1):11188. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67702-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32636402 Free PMC article.
-
A novel model for studying ileitis-induced visceral hypersensitivity in goats.Acta Vet Scand. 2016 Oct 6;58(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13028-016-0253-0. Acta Vet Scand. 2016. PMID: 27716368 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord astrocyte P2X7Rs mediate the inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on visceral hypersensitivity of rat with irritable bowel syndrome.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):43-53. doi: 10.1007/s11302-021-09830-6. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35389158 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral and Spinal Mechanisms Involved in Electro-Acupuncture Therapy for Visceral Hypersensitivity.Front Neurosci. 2021 Sep 28;15:696843. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.696843. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34658755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

