CHD6 eviction of promoter nucleosomes maintains housekeeping transcriptional program in prostate cancer
- PMID: 39717618
- PMCID: PMC11665337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102397
CHD6 eviction of promoter nucleosomes maintains housekeeping transcriptional program in prostate cancer
Abstract
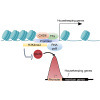
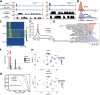
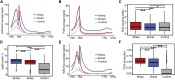
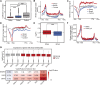
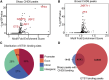
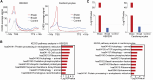
CHD6, a member of the chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein family, has been implicated in various diseases and tumors. However, its precise binding model of CHD6 on regulatory functional genes remains poorly understood. In this study, we discovered sharp peaks of CHD6, as the first member of CHD family for housekeeping process, binding only to the promoter region of genes in the C4-2 cell line. These genes, with conserved sharp CHD6 peaks across tumor cells, likely represent housekeeping genes ADNP and GOLGA5. Genes with sharp CHD6 peaks exhibit stable and low expression levels, sharing epigenetic features similar to housekeeping genes. Furthermore, this regulatory model also exists in both HEK293 cells and cardiomyocytes. Overall, the results of this study demonstrate that CHD6 binds to the promoter regions of housekeeping genes, regulating their histone modifications, chromatin structure, and gene expression.
Keywords: CHD6; MT: Bioinformatics; chromatin remodeling; epigenetics; histone modifications; housekeeping genes.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CHD6 promotes broad nucleosome eviction for transcriptional activation in prostate cancer cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 28;50(21):12186-12201. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1090. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36408932 Free PMC article.
-
The ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes CHD6, CHD7, and CHD8 exhibit distinct nucleosome binding and remodeling activities.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 14;292(28):11927-11936. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.779470. Epub 2017 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28533432 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin remodeler CHD6 promotes colorectal cancer development by regulating TMEM65-mediated mitochondrial dynamics via EGF and Wnt signaling.Cell Discov. 2022 Dec 6;8(1):130. doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00478-z. Cell Discov. 2022. PMID: 36473865 Free PMC article.
-
CHD chromatin remodelling enzymes and the DNA damage response.Mutat Res. 2013 Oct;750(1-2):31-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23954449 Review.
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
References
-
- Braga-Basaria M., Muller D.C., Carducci M.A., Dobs A.S., Basaria S. Lipoprotein profile in men with prostate cancer undergoing androgen deprivation therapy. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2006;18:494–498. - PubMed
-
- Rebello R.J., Oing C., Knudsen K.E., Loeb S., Johnson D.C., Reiter R.E., Gillessen S., Van der Kwast T., Bristow R.G. Prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021;7:9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

