Methodology for integrated analysis of vector- and spectroscopic bioimpedance methods
- PMID: 39717622
- PMCID: PMC11665879
- DOI: 10.2478/joeb-2024-0018
Methodology for integrated analysis of vector- and spectroscopic bioimpedance methods
Abstract
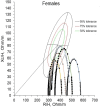
Electrical bioimpedance is based on the opposition exerted by body tissues to the passage of an electrical current. This characteristic allows the assessment of the individual's body composition, nutritional status, and hydration status. Electrical bioimpedance can be used to estimate body composition, health-related markers, general health status, diagnosis and prognostic of diseases, evaluation of treatment progress, and others. The aim of this study is to propose a methodology that allows us to integrate two methods of electrical bioimpedance analysis: bioelectrical impedance vector analysis, and bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy to evaluate the health of individuals. For methodology validation a retrospective clinical investigation was carried out where the data of healthy individuals and cancer patients included in the Database of the characterization of bioelectrical parameters by electrical Bioimpedance methods were analyzed. The values of electrical resistance and electrical reactance are higher in cancer patients compared to healthy individuals. However, the phase angle is lower in these patients. In the advanced stages of the disease, patients are located outside the tolerance ellipses. All these results are obtained at the characteristic frequency. The integration of bioelectrical impedance vector analysis, and bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy can be a sensitive complementary tool, capable of establishing differences between healthy individuals and cancer patients. Enrichment could be achieved by including the analysis of different physiological parameters through estimation equations validated by BIS parameters.
Keywords: Bioimpedance; body composition; tolerance ellipses.
© 2024 José Luis García Bello et al., published by Sciendo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of electrical bioimpedance vectors with the nutritional classification of vulnerable multiethnic children.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021 Dec;46:453-458. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.09.011. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021. PMID: 34857233
-
Bioelectrical impedance vector analysis and phase angle in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Food Nutr Res. 2019 Apr 10;63. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v63.1615. eCollection 2019. Food Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 31007651 Free PMC article.
-
Agreement of bioelectrical resistance, reactance, and phase angle values from supine and standing bioimpedance analyzers.Physiol Meas. 2021 Apr 6;42(3). doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/abe6fa. Physiol Meas. 2021. PMID: 33592586
-
Body fluid volumes measurements by impedance: A review of bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and bioimpedance analysis (BIA) methods.Med Eng Phys. 2008 Dec;30(10):1257-69. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.06.009. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Med Eng Phys. 2008. PMID: 18676172 Review.
-
Bioelectrical impedance analysis in clinical practice: a new perspective on its use beyond body composition equations.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2005 May;8(3):311-7. doi: 10.1097/01.mco.0000165011.69943.39. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2005. PMID: 15809535 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive classification and regression models for bioimpedance vector analysis: Insights from a southern Cuban cohort.J Electr Bioimpedance. 2025 Aug 4;16(1):89-98. doi: 10.2478/joeb-2025-0012. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Electr Bioimpedance. 2025. PMID: 40791222 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
