DIEP Flap Weights in Immediate 1-stage and 2-stage Breast Reconstruction: Considering Chest Wall Deformity
- PMID: 39717720
- PMCID: PMC11666181
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006393
DIEP Flap Weights in Immediate 1-stage and 2-stage Breast Reconstruction: Considering Chest Wall Deformity
Abstract
Background: There are advantages and disadvantages to both immediate 1-stage and 2-stage autologous-breast reconstruction. The 2-stage procedure may suffer from a hitherto overlooked difficulty: the tissue expander may induce chest wall depression that may require using a heavier-than-expected flap to generate symmetrical breasts. We conducted a retrospective observational study to assess this phenomenon.
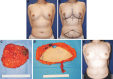
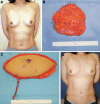
Methods: Consecutive patients who underwent 1-stage or 2-stage unilateral autologous-breast reconstruction with a deep inferior epigastric perforator flap were included. The 2 groups were compared in terms of age, body mass index, mastectomized tissue weight, inset-flap weight, and percentage additional flap weight (defined as [inset-mastectomy]/mastectomy × 100). The latter reflects the amount of additional flap tissue relative to mastectomized tissue that was needed to generate symmetrical breasts. The chest wall deformity after tissue expansion in the 2-stage patients was quantitated with computed tomography.
Results: Patients' healthy and affected breasts were symmetrical before surgery (P > 0.05). Compared with the 1-stage patients (n = 37), the 2-stage patients (n = 31) only differed in terms of a significantly higher mean percentage additional flap weight (28% versus 12%, P = 0.0077). Relative to preoperative values, nearly all 2-stage patients had mild (74%) or moderate (19%) chest wall deformity before tissue expander removal.
Conclusions: Due to tissue expander-induced chest wall deformity, 2-stage breast reconstruction may require a larger flap volume than is anticipated on the basis of preoperative volumetric measurements. Considering this phenomenon when choosing between immediate 1-stage and 2-stage reconstruction could potentially help improve patient outcomes.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Comparative Analysis of Sensory Return in Delayed-Immediate Versus Immediate Neurotized Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction.Ann Plast Surg. 2023 Mar 15. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003533. Online ahead of print. Ann Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 37115816
-
Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry?Breast J. 2016 Jan-Feb;22(1):75-82. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12515. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Breast J. 2016. PMID: 26534828 Clinical Trial.
-
A Comparison Between Immediate and Babysitter Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction in Postoperative Outcomes.Ann Plast Surg. 2022 May 1;88(3 Suppl 3):S179-S183. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003078. Ann Plast Surg. 2022. PMID: 35180751
-
Current status of autologous breast reconstruction in Argentina.Gland Surg. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):1814-1822. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-296. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39544967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application and prospect of preoperative computed tomographic angiography in deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap for breast reconstruction].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 15;34(7):927-931. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201907017. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32666740 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Koshima I, Soeda S. Inferior epigastric artery skin flaps without rectus abdominis muscle. Br J Plast Surg. 1989;42:645–648. - PubMed
-
- Gill P, Hunt J, Guerra A, et al. . A 10-year retrospective review of 758 DIEP flaps for breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113:1153–1160. - PubMed
-
- Nahabedian M, Momen B, Galdino G, et al. . Breast reconstruction with the free TRAM or DIEP flap: patient selection, choice of flap, and outcome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110:466–475. - PubMed
-
- Zhong T, Hu J, Bagher S, et al. . A comparison of psychological response, body image, sexuality, and quality of life between immediate and delayed autologous tissue breast reconstruction: a prospective long-term outcome study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138:772–780. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
