Pharmacological inhibition of the MAP2K7 kinase in human disease
- PMID: 39717752
- PMCID: PMC11663940
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1486756
Pharmacological inhibition of the MAP2K7 kinase in human disease
Abstract
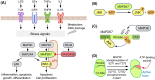
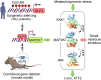
The MAP2K7 signaling pathway activates the c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase (JNK) in response to stress signals, such as inflammatory cytokines, osmotic stress, or genomic damage. While there has been interest in inhibiting JNK due to its involvement in inflammatory processes and cancer, there is increasing focus on developing MAP2K7 inhibitors to enhance specificity when MAP2K7 activation is associated with disease progression. Despite some progress, further research is needed to fully comprehend the role of MAP2K7 in cancer and assess the potential use of kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. This review examines the role of MAP2K7 in cancer and the development of small-molecule inhibitors.
Keywords: MAP2K7; T-ALL; cancer; kinase inhibitors; leukemia; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7.
Copyright © 2024 Lacorazza.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

