Entacapone alleviates muscle atrophy by modulating oxidative stress, proteolysis, and lipid aggregation in multiple mice models
- PMID: 39717825
- PMCID: PMC11663891
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1483594
Entacapone alleviates muscle atrophy by modulating oxidative stress, proteolysis, and lipid aggregation in multiple mice models
Abstract
Background: Skeletal muscle atrophy significantly affects quality of life and has socio-economic and health implications. This study evaluates the effects of entacapone (ENT) on skeletal muscle atrophy linked with oxidative stress and proteolysis.
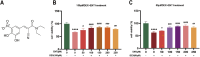
Methods: C2C12 cells were treated with dexamethasone (Dex) to simulate muscle atrophy. Four murine models were employed: diaphragm atrophy from mechanical ventilation, Dex-induced atrophy, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced atrophy, and hyperlipidemia-induced atrophy. Each model utilized entacapone (10 mg/kg), with sample sizes: Control (9), MV (11), MV + ENT (5) for diaphragm atrophy; Control (4), Dex (4), Dex + ENT (5) for Dex model; Control (4), LPS (4), LPS + ENT (5) for LPS model; and similar for hyperlipidemia. Measurements included muscle strength, myofiber cross-sectional area (CSA), proteolysis, oxidative stress markers [uperoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), uperoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE)], and lipid levels.
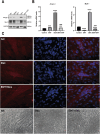
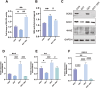
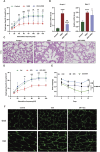
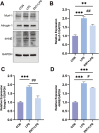
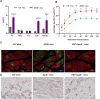
Results: Our findings confirm Dex-induced muscle atrophy, evidenced by increased expression of muscle atrophy-associated proteins, including Atrogin-1 and Murf-1, along with decreased diameter of C2C12 myotubes. Atrogin-1 levels rose by 660.6% (p < 0.05) in the Dex group compared to control, while entacapone reduced Atrogin-1 by 84.4% (p < 0.05). Similarly, Murf-1 levels increased by 365% (p < 0.05) in the Dex group and were decreased by 89.5% (p < 0.05) with entacapone. Dexamethasone exposure induces oxidative stress, evidenced by the upregulation of oxidative stress-related proteins Sod1, Sod2, and 4-HNE. Entacapone significantly reduced the levels of these oxidative stress markers, enhancing GSH-PX content by 385.6% (p < 0.05) compared to the Dex-treated group. Additionally, ENT effectively reduced the Dex-induced increase in MDA content by 63.98% (p < 0.05). Furthermore, entacapone effectively prevents the decline in diaphragm muscle strength and myofiber CSA in mice. It also mitigates diaphragm oxidative stress and protein hydrolysis. Additionally, entacapone exhibits the ability to attenuate lipid accumulation in the gastrocnemius muscle of hyperlipidemic mice and alleviate the reduction in muscle fiber CSA.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that entacapone is a promising therapeutic candidate for muscle atrophy, functioning through the reduction of oxidative stress, proteolysis, and lipid aggregation. Future research should explore the underlying mechanisms and potential clinical applications of entacapone in muscle-wasting conditions.
Keywords: entacapone; lipid aggregation; muscle atrophy; oxidative stress; proteolysis.
Copyright © 2024 Zeng, Xu, Wu, Zhou, Lei, Yu, Wang, Ma and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Morin attenuates dexamethasone-mediated oxidative stress and atrophy in mouse C2C12 skeletal myotubes.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021 Jun 15;704:108873. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2021.108873. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33848514
-
Neuron-derived neurotrophic factor protects against dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle atrophy.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Feb 19;593:5-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.01.028. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35051783
-
Anti-muscle atrophy effect of fermented Tenebrio molitor larvae extract by modulating the PI3K-Akt-mTOR/FoxO3α pathway in mice treated with dexamethasone.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Sep;178:117266. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117266. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39137649
-
Vigeo Promotes Myotube Differentiation and Protects Dexamethasone-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy via Regulating the Protein Degradation, AKT/mTOR, and AMPK/Sirt-1/PGC1α Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 13;16(16):2687. doi: 10.3390/nu16162687. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203823 Free PMC article.
-
Psoralea corylifolia L. seed extract attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy in mice by inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 5;296:115490. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115490. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35728709
Cited by
-
Sodium thiosulfate does not affect energy metabolism or organ (dys)function during resuscitation from murine trauma-and-hemorrhage.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025 Aug 6;13(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s40635-025-00778-0. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025. PMID: 40768004 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key modules and hub genes for sepsis-induced myopathy using weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 28;16:1607575. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1607575. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40792069 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

