Anticonvulsant effects of pentoxifylline on seizures induced by pentylenetetrazole and maximal electroshock in male mice: The role of the nitrergic pathway
- PMID: 39717871
- PMCID: PMC11664280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.11.013
Anticonvulsant effects of pentoxifylline on seizures induced by pentylenetetrazole and maximal electroshock in male mice: The role of the nitrergic pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Epilepsy remains a challenge, with one-third of patients experiencing refractory seizures despite current anti-seizure medications. The nitrergic system, which involves nitric oxide (NO) and NO synthase (NOS) enzymes, plays a complex role in seizure pathophysiology. Pentoxifylline (PTPh), an FDA-approved phosphodiesterase inhibitor, has anticonvulsant effects; however, its relationship with the pathway is unclear. This study focused at how the nitrergic system could be involved in PTPh's anticonvulsant effects.
Methods: Seizures were induced in male mice by intravenous pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) infusion (absence-like seizures), intraperitoneal PTZ injection, and maximal electroshock (generalized tonic-clonic seizures). PTPh was administered at various doses, alone or in combination with the NO precursor L-arginine, as well as non-selective (L-NAME) and selective NOS inhibitors (nNOS inhibitor 7-NI and iNOS inhibitor aminoguanidine). Seizure thresholds, latencies, incidence, and mortality were assessed. Moreover, in the next paradigm, using maximal electroshock model, we evaluate possible protective effects of PTPh against generalized tonic-clonic seizures and subsequent mortality.
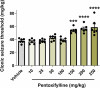
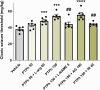
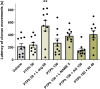
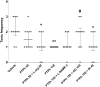
Results: In the intravenous PTZ model, PTPh (≥150 mg/kg) increased the seizure threshold, potentiated by L-arginine but reduced by L-NAME and 7-nitroindazole. In the intraperitoneal PTZ model, 150 mg/kg PTPh decreased tonic seizure frequency, which was mitigated by aminoguanidine. However, PTPh failed to prolong clonic seizure latency. In the maximal electroshock test, 100 mg/kg PTPh protected against tonic seizure incidence (reduced by aminoguanidine). Although PTPh could not reduce mortality, its combination with L-NAME or 7-nitroindazole increased mortality compared with the vehicle-treated group.
Conclusion: PTPh exerted anticonvulsant effects against absence-like and generalized tonic-clonic seizures, likely through modulation of the nitrergic system involving neuronal, endothelial, and inducible NOS isoform. These findings provide novel insights into the complex interplay between NO signaling and the anticonvulsant actions of PTPh, highlighting the potential therapeutic implications of targeting the NO pathway in epilepsy management.
Keywords: Dose-response; Maximal electroshock; Nitric oxide; Pentoxifylline; Pentylenetetrazole.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Abd Al Haleem E.N., et al. Possible protective effect of TNF-α inhibition and triad NO/cGMP/VEGF activation on gastric ulcer in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021;99(9):864–874. - PubMed
-
- Agbo J., et al. Therapeutic efficacy of voltage-gated sodium channel inhibitors in epilepsy. Acta Epileptol. 2023;5(1):16.
-
- Aghili S.H., et al. Mirtazapine improves locomotor activity and attenuates neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury in rats via neuroinflammation modulation. Neurochem Res. 2024 - PubMed
-
- Almostafa M.M., Mohamed M.E., Younis N.S. Ameliorative effects of vanillin against pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy and associated memory loss in mice: the role of Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 and HMGB1/RAGE/TLR4/NFκB pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024;129 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
