Insights into renal damage in hyperuricemia: Focus on renal protection (Review)
- PMID: 39717954
- PMCID: PMC11711934
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13424
Insights into renal damage in hyperuricemia: Focus on renal protection (Review)
Abstract
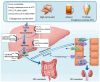
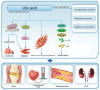
The incidence of hyperuricemia has increased recently, posing a serious threat to public health. Hyperuricemia is associated with an increased risk of gout, chronic kidney disease (CKD), obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypertriglyceridaemia, metabolic dysfunction‑associated steatotic liver disease, acute kidney injury, coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease (CVD). These diseases are commonly accompanied by varying degrees of kidney damage. A number of randomized controlled clinical trials have investigated the effectiveness of UA‑lowering therapies in preventing kidney disease progression. The present review provided fundamental insights into the pathogenesis, principles and therapeutic approaches for managing hyperuricemia in patients with aforementioned diseases and assesses the effect of uric acid‑lowering therapy on diabetic nephropathy, systemic lupus erythematosus, CKD, CVD and obesity progression.
Keywords: Hyperuricaemia; Uric acid; Renal damage; Urate-lowering therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yanai H, Adachi H, Hakoshima M, Katsuyama H. Molecular biological and clinical understanding of the pathophysiology and treatments of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:9221. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179221. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

