European Society for Gynaecological Endoscopy (ESGE) Good Practice Recommendations on surgical techniques for Removal of Fibroids: Part 2 Hysteroscopic Myomectomy
- PMID: 39718323
- PMCID: PMC11819789
- DOI: 10.52054/FVVO.16.4.054
European Society for Gynaecological Endoscopy (ESGE) Good Practice Recommendations on surgical techniques for Removal of Fibroids: Part 2 Hysteroscopic Myomectomy
Abstract
Submucosal uterine fibroids are the rarest type of fibroids. They can lead to abnormal uterine bleeding and may play a role in infertility and miscarriage. Hysteroscopic myomectomy is the preferred treatment to relieve bleeding caused by these fibroids and to restore the normal structure of the uterine cavity. The European Society for Gynaecological Endoscopy Uterine Fibroids Working Group developed recommendations based on the best available evidence and expert opinion for the surgical treatment of uterine fibroids. In this second part of the recommendations, hysteroscopic approaches are described. This review explores the techniques related to hysteroscopic myomectomy, focusing on narrower scopes, fluid management and advances in tissue removal systems and electrosurgery.
Figures
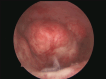


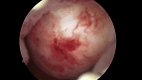

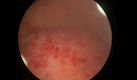

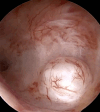


References
-
- AAGL Advancing Minimally Invasive Gynecology Worldwide, Munro MG, Storz K, et al. AAGL Practice Report: Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hysteroscopic Distending Media: (Replaces Hysteroscopic Fluid Monitoring Guidelines. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2000;7:167-168.) J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013;20:137–148. - PubMed
-
- AAGL. AAGL Practice Report: Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Submucous Leiomyomas. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:152–171. - PubMed
-
- Agostini A, Cravello L, Shojai R, et al. Postoperative infection and surgical hysteroscopy. Fertil Steril. 2002;77:766–768. - PubMed
-
- Bettocchi S, Ceci O, Di Venere R, et al. Advanced operative office hysteroscopy without anaesthesia: analysis of 501 cases treated with a 5 Fr. bipolar electrode. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:2435–2438. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
