Ultrasensitive Protein Aggregate Quantification Assays for Neurodegenerative Diseases on the Simoa Platform
- PMID: 39718440
- PMCID: PMC11740166
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c04188
Ultrasensitive Protein Aggregate Quantification Assays for Neurodegenerative Diseases on the Simoa Platform
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Ultrasensitive Protein Aggregate Quantification Assays for Neurodegenerative Diseases on the Simoa Platform".Anal Chem. 2025 Feb 25;97(7):4251. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c00703. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39930753 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
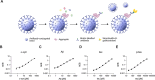
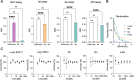
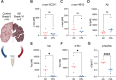
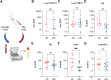
Nanoscale aggregates play a key role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. However, quantifying these aggregates in complex biological samples, such as biofluids and postmortem brain tissue, has been challenging due to their low concentration and small size, necessitating the development of methods with high sensitivity and specificity. Here, we have developed ultrasensitive assays utilizing the Quanterix Simoa platform to detect α-synuclein, β-amyloid and tau aggregates, including those with common posttranslational modifications such as truncation of α-synuclein and AT8 phosphorylation of tau aggregates. All assays had a detection limit in the low pM range. As a part of this work, we developed silica-nanoparticle calibrators, allowing for the quantification of all aggregates. These assays were validated for aggregate and target specificity through denaturation and cross-reactivity experiments. We then applied these assays to brain homogenate samples from Alzheimer's disease and control samples, demonstrating their applicability to postmortem tissue. Lastly, we explored the potential of these assays for blood-based diagnostics by detecting aggregates in serum samples from early Alzheimer's disease patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): D.B., M.R.C., E. F., D.K., J.Y.L.L., Y.W. and Z.X. are are inventors on patents filed based on this work.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong R. A. Plaques and Tangles and the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2006, 44 (1), 1–11. - PubMed
-
- De S.; Wirthensohn D. C.; Flagmeier P.; Hughes C.; Aprile F. A.; Ruggeri F. S.; Whiten D. R.; Emin D.; Xia Z.; Varela J. A.; Sormanni P.; Kundel F.; Knowles T. P. J.; Dobson C. M.; Bryant C.; Vendruscolo M.; Klenerman D. Different Soluble Aggregates of Aβ42 Can Give Rise to Cellular Toxicity through Different Mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10 (1), 1–11. 10.1038/s41467-019-09477-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

