Spasmodic dysphonia: the need for a combined neurological and phoniatric approach
- PMID: 39718622
- PMCID: PMC11909014
- DOI: 10.1007/s00702-024-02868-x
Spasmodic dysphonia: the need for a combined neurological and phoniatric approach
Abstract
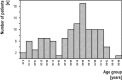
Spasmodic dysphonia (SD) is now generally considered to be a task-specific focal dystonia. For the first time, we wanted to explore the relationship between SD and dystonia from a combined neurological and phoniatric perspective. For this, we studied 115 patients with non-psychogenic SD by a combined neurological and phoniatric evaluation. Onset of SD was 49.7 ± 19.0 (6-68) years. The female/male ratio was 2. 63% had additional dystonia manifestations (cervical dystonia 35%, arm dystonia 15%, blepharospasm 11%, oromandibular dystonia 11%, writer's cramp 11%, pharyngeal dystonia 10%, generalised dystonia 4%, axial dystonia 2%, spasmodic dyspnoea 2% and segmental dystonia 1%). 71% occurred before, 25% after and 4% together with SD. 17% had a family history of dystonia and 6% a history of exposure to dopamine receptor blocking agents. 41% had mixed SD (SD-M), 31% abductor SD (SD-AB) and 28% adductor SD (SD-AD). SD-M was significantly correlated with additional dystonia manifestations and tremulous SD. No patient showed essential tremor or Parkinsonian syndromes. Two third of SD patients have additional dystonia manifestations and one fifth have a family history of dystonia, considerably more than previously described. In half of all patients, SD starts with non-SD dystonia. Our combined approach revealed a high prevalence of SD-M associated with frequent additional dystonia manifestations including dystonic tremor and a family history of dystonia. Patients presenting with SD should be evaluated for additional dystonia manifestations and dystonia patients should be evaluated for SD. Relevant coexistence of essential tremor and Parkinsonian syndromes cannot be confirmed.
Keywords: Abductor type; Adductor type; Dystonia; Essential tremor; Family history; Mixed type; Parkinsonian syndromes; Spasmodic dysphonia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: DD received honoraria for services provided to Allergan, Ipsen, Merz, Lanzhou Institute of Biological Products, Medy-Tox, Revance, Desitin, Syntaxin, AbbVie, Medtronic, St Jude, Boston Scientific, Almirall, Bayer, Sun, Teva, UCB, WizMedi, IAB-Interdisciplinary Working Group for Movement Disorders. He is shareholder of Allergan and holds patents on botulinum toxin and botulinum toxin therapy. FAS is founder and owner of IAB—Interdisciplinary Working Group for Movement Disorders. She received reimbursement from Abbot, AbbVie, Almirall, Allergan, Bayer, Desitin, Dynamed, Hempel GesundheitsPartner, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Licher, Meda, Medtronic, Merz, Orion, PTZ Nawrath, Sensomotorik & Rehabilitation Hellmuth & Thiel, Sintetica, Sporlastic, Sun, Teva, Tricumed, TRS Med, UCB. LP and BK have nothing to disclose.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources