Novel biomarkers for monitoring and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39719624
- PMCID: PMC11668010
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03600-1
Novel biomarkers for monitoring and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
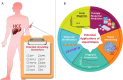
Due to current challenges in the early detection, less than 40% of individuals diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are viable candidates for surgical intervention. Therefore, validating and launching of a novel precise diagnostic approach is essential for early diagnosis. Based on developing evidence using circulating tumor cells and their derivatives, circulating miRNAs, and extracellular vesicles (EVs), liquid biopsy may offer a reliable platform for the HCC's early diagnosis. Each liquid biopsy analyte may provide significant areas for diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and treatment monitoring of HCC patients depending on its kind, sensitivity, and specificity. The current review addresses potential clinical applications, current research, and future developments for liquid biopsy in HCC management.
Keywords: Circulating tumor DNA; Circulating tumor cells; Extra-cellular vesicles; HCC biomarkers; Liquid biopsy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chouhan S, Singh S, Athavale D, Ramteke P, Vanuopadath M, Nair BG, et al. Sensitization of hepatocellular carcinoma cells towards doxorubicin and sorafenib is facilitated by glucosedependent alterations in reactive oxygen species, P-glycoprotein and DKK4. J Biosci. 2020;45:1. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

