Staged Screening Identifies People with Biomarkers Related to Neuronal Alpha-Synuclein Disease
- PMID: 39719857
- PMCID: PMC11889527
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.27158
Staged Screening Identifies People with Biomarkers Related to Neuronal Alpha-Synuclein Disease
Abstract
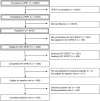
Objective: Remote identification of individuals with severe hyposmia may enable scalable recruitment of participants with underlying alpha-synuclein aggregation. We evaluated the performance of a staged screening paradigm using remote smell testing to enrich for abnormal dopamine transporter single-photon emission computed tomography imaging (DAT-SPECT) and alpha-synuclein aggregation.
Methods: The Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) recruited participants for the prodromal cohort who were 60-years and older without a Parkinson's disease diagnosis. Participants were invited to complete a University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test (UPSIT) independently through an online portal. Hyposmic participants were invited to complete DAT-SPECT, which determined eligibility for enrollment in longitudinal assessments and further biomarker evaluation including cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein seed amplification assay (aSynSAA).
Results: As of January 29, 2024, 49,843 participants were sent an UPSIT and 31,293 (63%) completed it. Of UPSIT completers, 8,301 (27%) scored <15th percentile. Of 1,546 who completed DAT-SPECT, 1,060 (69%) had DAT-SPECT binding <100% expected for age and sex. Participants with an UPSIT <10th percentile (n = 1,221) had greater likelihood of low DAT-SPECT binding compared to participants with an UPSIT in the 10th to 15th percentile (odds ratio, 3.01; 95% confidence interval, 1.85-4.91). Overall, 55% (198/363) of cases with UPSIT <15th percentile and DAT-SPECT <100% had positive aSynSAA, which increased to 70% (182/260) when selecting for more severe hyposmia (UPSIT <10th percentile).
Interpretation: Remote screening for hyposmia and reduced DAT-SPECT binding identifies participants with a high proportion positive aSynSAA. Longitudinal data will be essential to define progression patterns in these individuals to ultimately inform recruitment into disease modification clinical trials. ANN NEUROL 2025;97:730-740.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
C.S. is the Founder, Chief Scientific Officer, consultant, shareholder and member of the Board of Directors of Amprion, a biotech company focusing on the commercialization of the SAA technology for diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases, which was used for this analysis. L.C.M. is an employee of Amprion, holds stock options there, and holds United States Patents or patent application numbers 11,959,927, 11,970,520, 11,254,718, 20,210,164,998, 20,210,223,268, 20,190,353,669, 20,230,084,155, and 20,240,085,435, all assigned to Amprion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Conversion to Parkinson Disease in the PARS Hyposmic and Dopamine Transporter-Deficit Prodromal Cohort.JAMA Neurol. 2017 Aug 1;74(8):933-940. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.0985. JAMA Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28595287 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for alpha-synuclein aggregation in older individuals with hyposmia: a cross-sectional study.EBioMedicine. 2025 Feb;112:105567. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105567. Epub 2025 Feb 1. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39893720 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging prodromal Parkinson disease: the Parkinson Associated Risk Syndrome Study.Neurology. 2014 Nov 4;83(19):1739-46. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000960. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 25298306 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine transporter SPECT imaging in Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonian disorders.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Apr 30;51(2):400-410. doi: 10.3906/sag-2008-253. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33237660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine transporter (DAT) imaging in Parkinson's disease and related disorders.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2022 Jun;129(5-6):581-594. doi: 10.1007/s00702-021-02452-7. Epub 2021 Dec 15. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2022. PMID: 34910248 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying individuals at-risk of developing Parkinson's disease using a population-based recruitment strategy: The Healthy Brain Ageing Kassel Study.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Jul 18;11(1):216. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-01008-w. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40681552 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Associations of LILRB4 Genotypes With Parkinson's Disease: From Clinical Traits to Potential Pathologies.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70522. doi: 10.1111/cns.70522. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40702763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellomo G, De Luca CMG, Paoletti FP, et al. α‐Synuclein seed amplification assays for diagnosing Synucleinopathies: the way forward. Neurology 2022;99:195–205. - PubMed
-
- Iranzo A, Fairfoul G, Ayudhaya ACN, et al. Detection of α‐synuclein in CSF by RT‐QuIC in patients with isolated rapid‐eye‐movement sleep behaviour disorder: a longitudinal observational study. Lancet Neurol 2021;20:203–212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

