Undaria pinnatifida extract attenuates combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome by the modulation of epithelial cell dysfunction and oxidative stress
- PMID: 39719880
- PMCID: PMC12130702
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2024190
Undaria pinnatifida extract attenuates combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome by the modulation of epithelial cell dysfunction and oxidative stress
Abstract
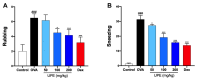
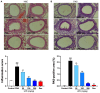
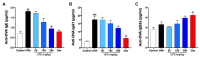
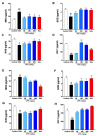
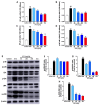
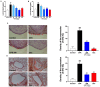
Undaria pinnatifida ( U. pinnatifida) has long been a part of the human diet and medicine. Although U. pinnatifida has been reported to have immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and antibacterial activities, its specific effect on patients with combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) has not been clarified. In this study, the anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects of U. pinnatifida extract (UPE) are investigated in a mouse model of ovalbumin (OVA)-induced CARAS. The oral administration of UPE inhibits allergic responses by reducing OVA-specific immunoglobulin levels. As a result, the symptoms of early reactions are also improved. UPE inhibits the accumulation of inflammatory cells and attenuates the expression of Th2 cytokines in both nasal and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Furthermore, UPE treatment inhibits the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway in lung homogenates. Additionally, UPE prevents shedding of the nasal mucosal epithelium, protects the integrity of the epithelium, enhances the expression of E-cadherin at the junction of epithelial cells, and inhibits the degradation of ZO-1 and occludin in the airway epithelium. In addition, UPE ameliorates dysfunction of the nasal epithelial barrier by enhancing antioxidant properties and downregulating the expression of the inflammatory factor IL-33. These results suggest that UPE may treat CARAS by modulating epithelial cell dysfunction and oxidative stress.
Keywords: IL-33; antioxidant; combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome; nasal epithelial barrier dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Undaria pinnatifida ameliorates nasal inflammation by inhibiting eosinophil and mast cell activation and modulating the NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Mar;12(3):e1215. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1215. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38488697 Free PMC article.
-
Piper Nigrum extract improves OVA-induced nasal epithelial barrier dysfunction via activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling.Cell Immunol. 2020 May;351:104035. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2019.104035. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Cell Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32051090
-
Fallopia japonica Root Extract Ameliorates Ovalbumin-Induced Airway Inflammation in a CARAS Mouse Model by Modulating the IL-33/TSLP/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 7;24(15):12514. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512514. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569890 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal administration of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides reduces lower airway inflammation in a murine model of combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Sep;28(1):390-8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.06.028. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26163938
-
CCR3 gene knockout in bone marrow cells ameliorates combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) by reducing airway inflammatory cell infiltration and Th2 cytokines expression in mice model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Mar;104:108509. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108509. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34998035
References
-
- Paiva Ferreira LKD, Paiva Ferreira LAM, Monteiro TM, Bezerra GC, Bernardo LR, Piuvezam MR. Combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) Int Immunopharmacol. . 2019;74:105718. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105718. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leynaert B, Neukirch F, Demoly P, Bousquet J. Epidemiologic evidence for asthma and rhinitis comorbidity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. . 2000;106:S201–S205. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.110151. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taramarcaz P, Gibson PG. The effectiveness of intranasal corticosteroids in combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome. Clin Exp Allergy. . 2004;34:1883–1889. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.02130.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cavalcanti RFP, Gadelha F, de Jesus TG, Cavalcante-Silva LHA, Paiva Ferreira LKD, Paiva Ferreira LAM, Vieira GC, et al. Warifteine and methylwarifteine inhibited the type 2 immune response on combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) experimental model through NF-кB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. . 2020;85:106616. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106616. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Liu C, Wu L, Zhu S. Potent ameliorating effect of Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) antagonist YC-1 on combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. . 2016;788:343–350. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.07.040. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

