The effects of different hormone combinations on the growth of Panax notoginseng anther callus based on metabolome analysis
- PMID: 39719933
- PMCID: PMC11667561
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1503931
The effects of different hormone combinations on the growth of Panax notoginseng anther callus based on metabolome analysis
Abstract
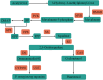
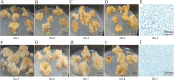
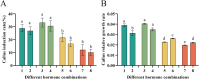
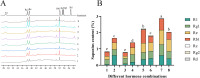
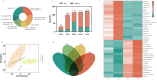
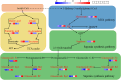
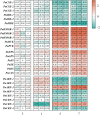
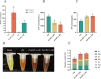
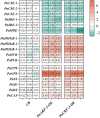
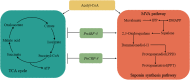
Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS), the primary active components of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H.Chen, a traditional and precious Chinese medicinal herb, are mainly derived from the roots of the plant. However, due to the long cultivation period and specific environmental requirements, the PNS supply is often limited. And, callus cultures of P. notoginseng, which grow rapidly, have short production cycles, and can be cultured under controlled conditions, provide a more efficient source for the quick acquisition of saponins. In this study, anthers of P. notoginseng were used as explants, and twelve hormone combinations were tested to induce callus formation. Eight kinds of hormone combinations successfully induced P. notoginseng anther callus. Among these, callus induced by combinations 5 and 7 had the highest saponin content, while those induced by combinations 1 and 3 exhibited the highest relative growth rates. Metabolomic analysis of these four callus types revealed that there were a total of 99 differential metabolites between combinations 5 and 7, 30 between combinations 1 and 3, 123 between combinations 3 and 7, and 116 between combinations 1 and 5. Further analysis showed that the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle metabolites in callus induced by combinations 1 and 3 were significantly upregulated, with corresponding genes showing high expression levels, increased ATP accumulation, and low responses of the auxin response factor PnARF-3 and cytokinin response factor PnCRF-3. The abundance of metabolites in the PNS biosynthesis pathway in callus induced by combinations 5 and 7 increased significantly, with related genes showing high expression levels, increased IPP accumulation, and high responses of PnARF-3 and PnCRF-3. Overexpression of PnARF-3 and PnCRF-3 in callus induced by combination 3 promoted the production of IPP and saponins while reducing ATP production. In conclusion, different hormone combinations affect the distribution of Acetyl-CoA through PnARF-3 and PnCRF-3, resulting in the relative growth rate and saponin of P. notoginseng anther callus differences.
Keywords: P. notoginseng callus; TCA cycle; auxin response factor; cytokinin response factor; saponin synthesis; secondary metabolite.
Copyright © 2024 Yu, Li, Liu, Li, Yang and Cui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

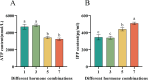
Similar articles
-
Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analysis reveals the regulatory mechanism of low nitrogen-driven biosynthesis of saponins and flavonoids in Panax notoginseng.Gene. 2024 Apr 5;901:148163. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148163. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Gene. 2024. PMID: 38224922
-
Chemosynthesis pathway and bioactivities comparison of saponins in radix and flower of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Apr 6;201:56-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Nov 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27838357
-
Impaired terpenoid backbone biosynthesis reduces saponin accumulation in Panax notoginseng under Cd stress.Funct Plant Biol. 2018 Jan;46(1):56-68. doi: 10.1071/FP18003. Funct Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30939258
-
Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jul 21;188:234-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27154405 Review.
-
Anti-diabetic potential of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS): a review.Phytother Res. 2014 Apr;28(4):510-6. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5026. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Phytother Res. 2014. PMID: 23846979 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

