Association between hypothyroidism and obstructive sleep apnea: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study combined with the geo database
- PMID: 39719972
- PMCID: PMC11666497
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1420391
Association between hypothyroidism and obstructive sleep apnea: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study combined with the geo database
Abstract
Background: The causal relationship between hypothyroidism and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) remains controversial. Therefore, our research used a bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) method in an attempt to determine the causal relationship between hypothyroidism and OSA.
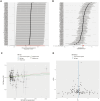
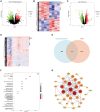
Methods: From the publicly accessible genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) summary database, we obtained single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) data pertaining to hypothyroidism and OSA. Inverse variance weighting (IVW) was the principal method of analysis utilized, with validation also conducted via weighted median, MR-Egger, simple model, and weighted model approaches. To further evaluate the robustness of the results, heterogeneity testing, pleiotropy testing, and the "leave-one-out" sensitivity analysis were performed. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the OSA dataset (GSE135917) and hypothyroidism dataset (GSE176153) derived from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database were screened using the "limma" package. The "clusterProfiler" and "GO plot" packages were used for further enrichment analysis in order to validate the findings of the MR study. The Cytoscape software was utilized to build a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of DEGs and to screen for hub genes.
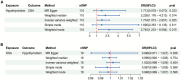
Results: The MR analysis showed that genetically predicted hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk of OSA [IVW odds ratio (OR) = 1.734; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.073-2.801; p = 0.025]. The trend of the outcomes of the other approaches is consistent with the trend of the IVW outcome. However, the reverse MR analysis suggested no evidence for the causal effect of OSA on hypothyroidism (IVW OR = 1.002, 95% CI: 0.996-1.009, p = 0.454). The robustness of the results was confirmed by the sensitivity analysis. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that there were DEGs that hypothyroidism and OSA have in common.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that hypothyroidism may increase the risk of OSA, while the effect of OSA on hypothyroidism was not found in this MR study. Thus, patients with hypothyroidism should be enhanced with screening for OSA for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Keywords: GEO; Mendelian randomization; causality; hypothyroidism; obstructive sleep apnea.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Huang, Zheng, Cai, Han, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

