Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Modulates the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway in Experimental Necrotizing Enterocolitis
- PMID: 39719983
- PMCID: PMC11668547
- DOI: 10.1155/mi/4811500
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Modulates the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway in Experimental Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Abstract
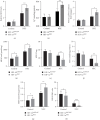
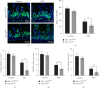
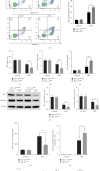
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating disease observed in premature infants, characterized by intestinal ischemia and inflammation. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α), a master regulator of the cellular response to hypoxia and ischemia, plays a critical role in NEC pathogenesis. However, the precise mechanisms by which HIF-1α influences the intestines in NEC remain poorly understood. Herein, we aimed to explore the role of HIF-1α in NEC using a transgenic mouse model. We induced NEC in neonatal mice from postnatal day 5 to 9, and various parameters, including intestinal injury, oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) proliferation, and apoptosis, were assessed. The results confirmed that the absence of intestinal epithelial HIF-1α increased the susceptibility of mice to NEC-induced intestinal injury, as evidenced by increased oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, apoptosis, and inhibition of proliferation. Additionally, we observed an upregulation of the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway specifically in the intestines of mice lacking HIF-1α in IECs (HIF-1αΔIEC) with NEC. These findings provide crucial insights into the role of HIF-1α in regulating intestinal oxidative stress and inflammation to maintain intestinal homeostasis, highlighting its association with the TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway. Furthermore, these insights might lead to the identification of novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of NEC.
Keywords: NF-κB; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; inflammation; necrotizing enterocolitis; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2024 Yunfei Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

