Menaquinone-7 and its therapeutic potential in type 2 diabetes mellitus based on a Zucker diabetic fatty rat model
- PMID: 39719993
- PMCID: PMC11666950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40826
Menaquinone-7 and its therapeutic potential in type 2 diabetes mellitus based on a Zucker diabetic fatty rat model
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is marked by insulin resistance, low grade chronic inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction. Vitamin K2, especially menaquinone-7 (MK-7), might delay T2DM progression and alleviate its consequences. Hence, this study evaluated the effects of MK-7 on serum and urine markers of diabetes in an animal model of T2DM.
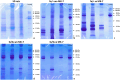
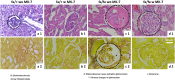
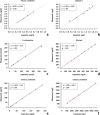
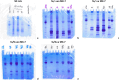
Methods: Hetero- (fa/+, control) and homozygous (fa/fa, diabetic) male Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats were supplemented or not with MK-7 for 12 weeks. After euthanasia, vitamin K1, menaquinone-4 and MK-7 serum concentrations were analyzed via reversed phase high pressure liquid chromatography. Glucose (serum), fructosamine (serum) and creatinine (serum and urine) levels were assessed photometrically, serum cystatin C and urinary total protein were turbidimetrically determined. Serum transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) and procollagen type III N-terminal peptide (PIIINP) were quantified with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Urinary marker proteins were analyzed via sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nephropathy was assessed histologically.
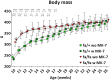
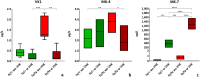
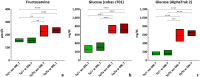
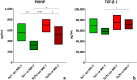
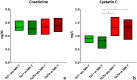
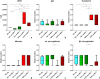
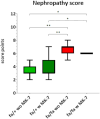
Results: Supplementation led to significantly elevated MK-7 serum levels and a significant reduction of PIIINP serum levels in both hetero- and homozygous ZDF rats. Additionally, not statistically significant reductions of TGF-β1 serum levels, proteinuria as well as the nephropathy score were observed. In vivo body mass, serum fructosamine, glucose, cystatin C and creatinine levels were unaffected.
Conclusion: MK-7 reduced serum markers of fibrosis, histological features of nephropathy and urinary protein excretion, but failed to affect serum markers of T2DM. The therapeutic potential of MK-7 in T2DM and its mode of action should be further investigated in more detail.
Keywords: Menaquinone-7; Nephropathy; Procollagen type III N-Terminal peptide (PIIINP); Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1); Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rice endosperm protein slows progression of fatty liver and diabetic nephropathy in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.Br J Nutr. 2016 Oct;116(8):1326-1335. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516003512. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27724997
-
Differences in plasma homocysteine levels between Zucker fatty and Zucker diabetic fatty rats following 3 weeks oral administration of organic vanadium compounds.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2006;19(4):251-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2005.10.001. Epub 2005 Dec 13. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 16443173
-
Vasopeptidase inhibition prevents nephropathy in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2003 Nov 1;60(2):447-54. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(03)00544-3. Cardiovasc Res. 2003. PMID: 14613875
-
Urinary cystatin C as a biomarker for diabetic nephropathy and its immunohistochemical localization in kidney in Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013 Jul;65(5):615-22. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 22795897
-
Podocyte injury promotes progressive nephropathy in zucker diabetic fatty rats.Lab Invest. 2002 Jan;82(1):25-35. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3780392. Lab Invest. 2002. PMID: 11796823
Cited by
-
Differential Responses of Articular Chondrocytes from Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Rats to Glucose Conditions and Inflammatory Stimuli: Influence of a Vitamin K2 Enriched Diet.Cartilage. 2025 Mar 21:19476035251317091. doi: 10.1177/19476035251317091. Online ahead of print. Cartilage. 2025. PMID: 40119526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . Diabetes Atlas. tenth ed. 2021. https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/ Available from:
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

