Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicity of the genus Gouania
- PMID: 39720023
- PMCID: PMC11665460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40933
Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicity of the genus Gouania
Abstract
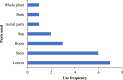
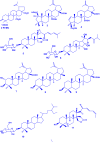
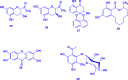
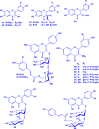
The genus Gouania (Rhamnaceae) comprises at least 50 recognized species distributed across tropical and subtropical regions. Gouania species have been ethnomedicinally used to treat a variety of ailments. Despite their widespread medicinal use, there is no comprehensive documentation that consolidates the ethnobotanical knowledge, phytochemicals, pharmacological properties, and toxicity of Gouania species. Herein, this review details the ethnopharmacology, phytochemical constituents, pharmacological properties and toxicity of Gouania species to provide perspectives for future research on this genus. Based on available literature, herbal preparations from Gouania species have been used to treat ailments related to the digestive, cardiovascular, respiratory, skin, musculoskeletal, reproductive, endocrine and urological systems. Extracts and isolated compounds from seven Gouania species (G. leptostachya, G. longipetala, G. lupulozdes, G. macrocarpa, G. longispicata, G. obtusifolia, and G. ulmifolia) have demonstrated promising anticancer, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antiviral properties, supporting their ethnomedicinal uses. To date, 64 compounds (including 6 phenolic compounds, 24 flavonoids, and 34 terpenoids) have been isolated and characterized in the genus mainly as gouaniasides I-IX, gouanogenins, and gouanic acids. Most Gouania species remain unexplored for their potential bioactivities. The identification of more than 54 % as novel compounds from just seven Gouania species highlights the genus as a promising source for discovering new therapeutic agents to combat the growing challenge of multidrug-resistant pathogens. Conducting extensive phytochemical and pharmacological analyses across a broader array of Gouania species could unveil a more comprehensive profile of bioactive compounds, and pave way for innovative treatments against a diverse range of pathogens and diseases.
Keywords: Acute toxicity; Gouania longipetala; Gouaniasides; Gouanic acids; Gouanogenin.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Hannington Gumisiriza reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100009915Mbarara University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Science. Hannington Gumisiriza reports a relationship with 10.13039/501100009915Mbarara University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Science that includes: funding grants. All authors have no conflict. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The genus Actinidia Lindl. (Actinidiaceae): A comprehensive review on its ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 2):117222. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117222. Epub 2023 Oct 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37793579 Review.
-
Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of the genus Sambucus L. (Viburnaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jun 28;292:115102. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115102. Epub 2022 Mar 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35288288 Review.
-
A review of the ethnomedicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacological properties of the genus Acanthus (Acanthaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115271. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115271. Epub 2022 Apr 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35430290 Review.
-
The genus Nepeta: Traditional uses, phytochemicals and pharmacological properties.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;268:113679. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113679. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33307050 Review.
-
Phytochemistry and pharmacology of the genus Drypetes: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 22;190:328-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.060. Epub 2016 Jun 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27353868 Review.
References
-
- Thuy N.T.K., Trang D.T., Thi M., Trang N., Bay N.K., Tai B.H. Flavonol glycosides and dammarane saponin from Gouania leptostachya. Vietnam J. Chem. 2019;57(3):277–280. doi: 10.1002/vjch.201960026. - DOI
-
- Jacquin N.J. 1763. Selectarum Stirpium Americanarum Historia. Ex Officina Krausiana. Vindobonae [Wien]
-
- Pool A. Taxonomic revision of Gouania (rhamnaceae) for north America. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2014;99(3):490–552. doi: 10.3417/2013016. - DOI
-
- Endlicher S. Beck; Wien: 1840. Rhamneae: Genera Plantarum Secundum Ordines Naturales Disposita; pp. 1094–1105.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

