Progress in photocatalytic degradation of industrial organic dye by utilising the silver doped titanium dioxide nanocomposite
- PMID: 39720083
- PMCID: PMC11667620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40998
Progress in photocatalytic degradation of industrial organic dye by utilising the silver doped titanium dioxide nanocomposite
Abstract
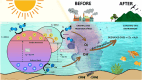
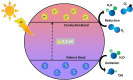
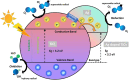
Industrial organic dyes represent a significant portion of pollutants discharged into the environment, particularly by the textile industry. These compounds pose serious threats to living organisms due to their high toxicity. Various techniques have been explored for the degradation of organic dyes, among which heterogeneous photocatalysis utilising titanium dioxide (TiO2) stands out as a promising technology. However, the practical application of TiO2 as photocatalyst has limitations for the following reasons; First, TiO2 has a low sensitivity to visible light due to a large band gap which can be 3.2 eV for the anatase polymorph. Second, the recombination rate of photo-induced electron-hole pairs in TiO2 is very fast. Recent research studies have brought to light that a silver-doped titanium dioxide nanocomposite could be one of the promising answers to these problems. This nanocomposite has garnered significant attention because of its unique features that suggest the manifestation of more effective concepts to minimize the electron-hole recombination and broaden light absorption. This causes Schottky barrier which is essentially created by integrating the silver nanoparticles into titanium dioxide. It is quite significant in decelerating the recombination of the electron-hole pairs, thus increasing photocatalytic activity. Further, it is more effective in that the use of silver also widens the titanium dioxide absorption range to the visible light hence maximizing capture and conversion of broader range of light energies for catalytic reactions. This paper therefore seeks to examine the research background regarding the industrial organic dyes starting with the history of industrial organic dyes before delving into an evaluation of the current and most current research on industrial organic dyes looking at advanced methods of their degradation with specific focus on silver-doped TiO2 for photocatalytic enhancement. This paper also reviews the experimental work concerning the actual photocatalytic degradation process and presents the factors affecting the performance of silver-doped TiO2 nanocomposites by eliminating organic dyes from wastewater. It also encompasses a general background into the various synthesis methods used in the preparation of silver-doped TiO2 nanocomposites. Additionally, challenges and future perspectives in the field are outlined, with a focus on the development of novel strategies to further improve the efficiency and sustainability of silver-doped TiO2 photocatalysts for industrial organic dye degradation. In conclusion, this review offers a significant outlook on the existing literature concerning the silver-doped TiO2 nanocomposites for effective photocatalytic degradation of the industrial organic dyes because of the rising pollution level and helping future researchers in seeking the solutions for environmental issues and developing sustainable wastewater treatment.
Keywords: Nanocomposite; Organic dye; Photocatalytic degradation; Silver; Titanium dioxide.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Chin Wei Lai reports financial support was provided by Higher Education Center of Excellence (HICoE). Chin Wei Lai reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100023431Universiti Malaya Research Excellence Grant (UMREG). Chin Wei Lai reports financial support was provided by Global Collaborative Programme -SATU Joint Research Scheme. Chin Wei Lai reports financial support was provided by Deanship of Research and Graduate Studies. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent progress on Ag/TiO2 photocatalysts: photocatalytic and bactericidal behaviors.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Sep;28(33):44638-44666. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14996-y. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34212334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photodegradation of organic water pollutants under visible light using anatase F, N co-doped TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite: Semi-pilot plant experiment and density functional theory calculations.Chemosphere. 2021 Jul;275:129903. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129903. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Chemosphere. 2021. PMID: 33647684
-
C, F co-doping Ag/TiO2 with visible light photocatalytic performance toward degrading Rhodamine B.Environ Res. 2023 Sep 1;232:116311. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116311. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37290622
-
Photocatalytic degradation of azo and anthraquinone dye using TiO2/MgO nanocomposite immobilized chitosan hydrogels.Environ Technol. 2021 Jun;42(15):2278-2291. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2019.1701094. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Environ Technol. 2021. PMID: 31810416
-
Investigation of TiO2/PPy nanocomposite for photocatalytic applications; synthesis, characterization, and combination with various substrates: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jun;31(30):42521-42546. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-33893-8. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38878243 Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming henna: from natural dye to photosensitizer for efficient photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol using a green-synthesized ZnO@henna nanocomposite.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 2;15(23):18245-18265. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02154e. eCollection 2025 May 29. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40458432 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical Properties and Multifunctional Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 27;26(13):6222. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136222. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ce-doped nano-Fe-TiO2 composites for photocatalytic degradation of naphthol blue black in aqueous medium.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 17;15(31):25322-25336. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02583d. eCollection 2025 Jul 15. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40677944 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of ZnS/MoS2-decorated porous carbon for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08920-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593117 Free PMC article.
-
Copper-based nanoparticles for the removal of the crystal violet dye via degradation and adsorption: a comparative account.RSC Adv. 2025 Aug 6;15(34):27995-28020. doi: 10.1039/d5ra04003e. eCollection 2025 Aug 1. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40772009 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; 2019. 1 in 3 People Globally Do Not Have Access to Safe Drinking Water – UNICEF, WHO.https://www.who.int/news/item/18-06-2019-1-in-3-people-globally-do-not-h...
-
- Okafor C.C., Madu C.N., Ajaero C.C., Ibekwe J.C., Nzekwe C.A. Sustainable management of textile and clothing. Clean Technologies and Recycling. 2021;1(1):70–87. doi: 10.3934/ctr.2021004. - DOI
-
- Maheshwari K., Agrawal M., Gupta A.B. Dye pollution in water and wastewater. Sustainable Textiles: Production, Processing, Manufacturing & Chemistry. 2021:1–25. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-2892-4_1. - DOI
-
- Bailey K., Basu A., Sharma S. The environmental impacts of fast fashion on water quality: a systematic review. Water. 2022;14(7):1073. doi: 10.3390/w14071073. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

