Impact of telehealth-based therapeutic exercise on pain, functional performance and dynamic knee valgus in young adult females with patellofemoral pain: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 39720152
- PMCID: PMC11667270
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjsem-2024-001939
Impact of telehealth-based therapeutic exercise on pain, functional performance and dynamic knee valgus in young adult females with patellofemoral pain: a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a telehealth-based therapeutic exercise (TTE) programme with real-time video conference supervision for young adult females with patellofemoral pain (PFP).
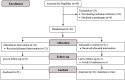
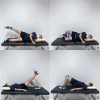
Methods: The study design was a randomised controlled trial. Forty-two participants with PFP were allocated to either the TTE group or the control (C) group. The TTE group received a 4-week telehealth-based exercise programme supervised through real-time video conferencing, while the C group followed a self-guided stretching exercise. Pain intensity was assessed using the Visual Analogue Scale, while functional performance was evaluated with hop tests and the step-down test. Dynamic knee valgus was measured by the frontal plane projection angle during a single-leg squat. In addition, the study used a specific health questionnaire which evaluated knee pain and function, including the self-administered Kujala Patellofemoral Questionnaire (KPQ). All outcomes were assessed both before and after the intervention.
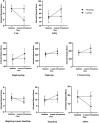
Results: After the 4-week interventions, the results showed a significant interaction between the group and the time of pain intensity, functional performance and dynamic knee valgus (p<0.001). The TTE group demonstrated significant pain reduction (p<0.001) and improved KPQ score (p<0.001), while the C group showed no significant changes. TTE participants also exhibited improved functional performance in the hop and step-down tests. Additionally, dynamic knee valgus was significantly decreased in the TTE group.
Conclusion: The telehealth-based exercise programmes offer a convenient and effective alternative for managing PFP symptoms, providing remotely accessible and specialised care.
Keywords: Exercise rehabilitation; Knee; Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome; Performance.
Copyright © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Nilmart P, Yodchaisarn W, Vongsirinavarat M, et al. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome in Young Adult Women With Low to Moderate Physical Activity Levels. IRJ . 2022;20:99–108. doi: 10.32598/irj.20.1.1565.1. - DOI
-
- Gaitonde DY, Ericksen A, Robbins RC. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99:88–94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
