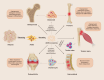
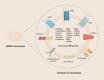
Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as Nanocarriers for Treating Musculoskeletal Disorders
- PMID: 39720215
- PMCID: PMC11668248
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S486622
Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as Nanocarriers for Treating Musculoskeletal Disorders
Abstract
Musculoskeletal disorders are a series of diseases involving bone, muscle, cartilage, and tendon, mainly caused by chronic strain, degenerative changes, and structural damage due to trauma. The disorders limit the function of patients due to pain and significantly reduce their quality of life. In recent years, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells have been extensively applied in regeneration medicine research due to their particular abilities of self-renewal, differentiation, and targeted homing and are more easily accessed compared with other sources. The paracrine effect of ADSCs plays a crucial role in intercellular communication by releasing mass mediators, including cytokines and growth factors, particularly the exosomes they secrete. Not only do these exosomes possess low immunogenicity, low toxicity, and an enhanced ability to penetrate a bio-barrier, but they also inherit their parent cells' characteristics and carry various bioactive molecules to release to targeted cells, modulating their biological process. Meanwhile, these characteristics also make exosomes a natural nanocarrier capable of targeted drug delivery to specific sites, enhancing the bioavailability of drugs within the body and achieving precision therapy with fewer toxic side effects. Furthermore, the integration of exosomes with tissue engineering and chemical modification strategies can also significantly enhance their efficacy in facilitating tissue repair. However, the current research on ADSC-Exos for improving MSDs remains at an early stage and needs further exploration. Therefore, this review summarized the ADSC-Exo as a nanodrug carrier characteristics and mechanism in the treatment of fracture, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, intervertebral disc degeneration, and tendon injury, which push forward the research progress of ADSC-Exo therapy for MSDs.
Keywords: adipose mesenchymal stem cells; exosomes; musculoskeletal disorders; regenerative medicine.
© 2024 Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Applications of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell (ADSC) Exosomes in Tissue Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 29;25(11):5916. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115916. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes promote tendon healing by activating both SMAD1/5/9 and SMAD2/3.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jun 10;12(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02410-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34112236 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes derived from minor salivary gland mesenchymal stem cells: a promising novel exosome exhibiting pro-angiogenic and wound healing effects similar to those of adipose-derived stem cell exosomes.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Dec 3;15(1):462. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04069-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39627883 Free PMC article.
-
Co-transplantation of exosomes derived from hypoxia-preconditioned adipose mesenchymal stem cells promotes neovascularization and graft survival in fat grafting.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Feb 26;497(1):305-312. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.076. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29428734
-
The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Aug 7;10(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1358-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31391108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of IER3 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 12;13(4):947. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040947. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299640 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome‑mediated crosstalk between the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Sep;56(3):129. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5570. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40576128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes Extracted from Human Umbilical Cord MSCs Contribute to Osteoarthritic Cartilage and Chondrocytes Repair Through Enhancing Autophagy While Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Jul;22(5):719-733. doi: 10.1007/s13770-025-00716-x. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 40232653
References
-
- Reddy MZAP. Stem Cells for Treatment of Musculoskeletal Conditions - Orthopaedic/Sports Medicine Applications. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866:165624. - PubMed
-
- Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Cross M, et al. Prevalence, Deaths, and Disability‐Adjusted Life Years Due to Musculoskeletal Disorders for 195 Countries and Territories 1990–2017. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2021;73:702–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources