LncRNA DLEU1 contributes to the progression of septic myocardial dysfunction by targeting miR-381-3p
- PMID: 39720275
- PMCID: PMC11664811
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2024.144199
LncRNA DLEU1 contributes to the progression of septic myocardial dysfunction by targeting miR-381-3p
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiac dysfunction is a common complication of sepsis. This study aimed to elucidate the regulatory effect of DLEU1 on sepsis-induced myocardial injury.
Material and methods: HL-1 cardiomyocytes were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to mimic sepsis-induced myocardial injury in vitro, and the mouse septic model was established through cecum ligation and perforation (CLP). Cell viability was evaluated using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), while apoptosis was assessed via Annexin-V staining. Pro-inflammatory factors including tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1 β, IL-6, and oxidative stress indicators were detected by ELISA kits. Cardiac function in mice was determined using cardiac ultrasound, and myocardial indices were detected by ELISA.
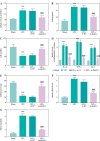
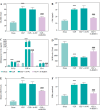
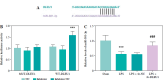
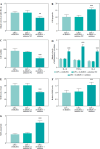
Results: DLEU1 levels were up-regulated gradually in HL-1 cardiomyocytes after LPS treatment in a dose-dependent manner, along with the overactivation of inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. DLEU1 downregulation alleviated LPS-induced cell apoptosis, inflammatory response and oxidative stress. In vivo, DLEU1 knockdown improved the cardiac function of septic mice, and alleviated inflammation and oxidative stress. MiR-381-3p, acting as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) of DLEU1, reversed the effects of DLEU1 in both septic cell and mouse models.
Conclusions: The results indicate that the DLEU1/miR-381-3p axis is an intrinsic regulator of myocardial injury in sepsis.
Keywords: DLEU1; inflammation; miR-381-3p; myocardial injury; sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SP1-induced ZFAS1 aggravates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via miR-590-3p/NLRP3-mediated autophagy and pyroptosis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Nov 30;695:108611. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108611. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 33002446
-
Long noncoding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by improving inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function through mediating the miR-501-3p/CADM1/STAT3 axis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Feb 15;128:111500. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111500. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38237222
-
Inhibition of miR-103a-3p suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis and liver injury by regulating FBXW7 expression.Cell Biol Int. 2020 Sep;44(9):1798-1810. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11372. Epub 2020 May 12. Cell Biol Int. 2020. PMID: 32369227 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA NEAT1 promotes the progression of sepsis-induced myocardial cell injury by sponging miR-144-3p.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jan;24(2):851-861. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202001_20069. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32016991
-
Circ_0114428 Regulates Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury by Targeting the miR-495-3p/CRBN Axis.Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44(4):1464-1477. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01432-z. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33830389
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
