Impacts of social isolation stress in safety learning and the structure of defensive behavior during a spatial-based learning task involving thermal threat
- PMID: 39720306
- PMCID: PMC11666493
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1503097
Impacts of social isolation stress in safety learning and the structure of defensive behavior during a spatial-based learning task involving thermal threat
Abstract
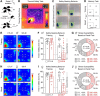
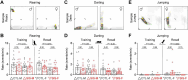
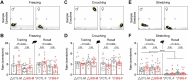
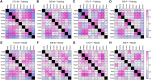
Safety learning during threat and adversity is critical for behavioral adaptation, resiliency, and survival. Using a novel mouse paradigm involving thermal threat, we recently demonstrated that safety learning is highly susceptible to social isolation stress. Yet, our previous study primarily considered male mice and did not thoroughly scrutinize the relative impacts of stress on potentially distinct defensive mechanisms implemented by males and females during the thermal safety task. The present study assessed these issues while considering a variety of defensive behaviors related to safety-seeking, escape, coping, protection, ambivalence, and risk-taking. After a two-week social isolation stress period, mice were required to explore a box arena that had thermal threat and safety zones (5 vs. 30°C, respectively). Since visuospatial cues clearly differentiated the threat and safety zones, the majority of the no-stress controls (69-75%) in both sexes exhibited optimal memory formation for the safety zone. In contrast, the majority of the stress-exposed mice in both sexes (69-75%) exhibited robust impairment in memory formation for the safety zone. Furthermore, while the control groups exhibited many robust correlations among various defensive behaviors, the stress-exposed mice in both sexes exhibited disorganized behaviors. Thus, stress severely impaired the proper establishment of safety memory and the structure of defensive behavior, effects that primarily occurred in a sex-independent manner.
Keywords: anxiety; behavioral flexibility; conflict; decision making; fear; prefrontal cortex (PFC).
Copyright © 2024 Villalon, Felix-Ortiz, Lozano-Ortiz, McCarrey and Burgos-Robles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Altmann J. (1974). Observational study of behavior: sampling methods. Behaviour 49 227–267. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™, 5th Edn. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc. 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

