Applicability of creatinine-based glomerular filtration rate assessment equations to patients with neurogenic bladder
- PMID: 39720311
- PMCID: PMC11667110
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1501161
Applicability of creatinine-based glomerular filtration rate assessment equations to patients with neurogenic bladder
Abstract
Purpose: Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measured by dynamic renal scintigraphy (Gates method) is used in this study as the standard to investigate the applicability of two creatinine (Cr)-based GFR estimation equations in Chinese patients of different genders, age groups, and GFR stages diagnosed with neurogenic bladder (NB).
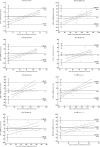
Methods: GFR values were measured using 99mTc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging, the new serum creatinine (Cr)-based chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaborative group (CKD-EPI) equation, and the equation for the estimated GFR of CKD patients in China, which were designated as sGFR, EPI-GFR, and cGFR, respectively. Pearson's correlation and linear regression were used to compare the differences, absolute differences, precision, and accuracies of the results of the two equations with sGFR to determine the formula offering better performance for the assessment of patients with NB.
Results: Measurements from a total of 99 patients with NB were used in the final analysis. Both cGFR and EPI-GFR were moderately correlated with sGFR in both men and women. The overall staging accuracies of EPI-GFR and sGFR were significantly higher than that of cGFR. Among the patients staged, only those with GFRs in the range of 60-89 mL/min/1.73 m2 had moderate correlations between cGFR, EPI-GFR, and sGFR, while the remaining patients had low correlations.
Conclusion: Researchers found that the equation developed for Chinese CKD patients performed well for patients with NB aged 20-25 years, while the race-neutral CKD-EPI equation performed better in NB patients aged 26-35 years.
Keywords: 99mTc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging; glomerular filtration rate; neurogenic bladder; renal function; serum creatinine.
Copyright © 2024 He and Liao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Creatinine-based equations to estimate glomerular filtration rate should be used with caution in patients with neurogenic bladder.Clin Nephrol. 2023 May;99(5):219-227. doi: 10.5414/CN111011. Clin Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36871228
-
[The application of glomerular filtration rate estimation equations in different stages of chronic kidney disease].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Apr;44(4):285-9. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15924645 Chinese.
-
Is the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration four-level race equation better than the cystatin C equation?Nephrology (Carlton). 2012 May;17(4):407-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2012.01568.x. Nephrology (Carlton). 2012. PMID: 22257305
-
GFR estimation: from physiology to public health.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 May;63(5):820-34. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.12.006. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24485147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic value of the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equations in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2020 Jun;48(6):300060520925950. doi: 10.1177/0300060520925950. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32589856 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources