Evaluating Emotional Intelligence in Medical Students: A Comparative Analysis of Their Trait Emotional Intelligence (TEI) Scores Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 39720382
- PMCID: PMC11667645
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74335
Evaluating Emotional Intelligence in Medical Students: A Comparative Analysis of Their Trait Emotional Intelligence (TEI) Scores Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
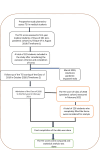
Medical education, which generally relied heavily on intelligence quotients, has found a new value in emotional intelligence (EI), specifically after the challenges faced during the COVID-19 pandemic. The COVID-19 pandemic has had some apparent and some intangible effects, as this required an emergency switch to online teaching and learning. Aim: This study was conducted to compare the trait emotional intelligence (TEI) score of medical undergraduates with the increasing number of years of medical curriculum. The COVID-19 pandemic serendipitously provided an opportunity to compare the TEI scores in pre-pandemic and during pandemic times. Materials and methods: Trait emotional intelligence was computed using a pre-validated Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire-Short Form (TEIQue-SF). The study was conducted in two time frames and in two study groups, the Class of 2019 (pre-pandemic cohort) and the Class of 2020 (pandemic cohort). Further, the pre-pandemic cohort's EI score was assessed twice, initially in August 2019 (Timeframe 1 (T1) which was before the pandemic) and secondly in October 2020 (Timeframe 2 (T2) which was during the pandemic) in Phase II and the COVID-19 first wave was peaking in India. The TEI scores of the pre-pandemic cohort and pandemic cohort were compared using an unpaired T-test. The pre-pandemic cohort scores assessed in two time frames were compared using a paired T-test. Results: The pandemic cohort showed significantly less total TEI (p < 0.05) and well-being score (p < 0.05) in the pre-pandemic cohort from August 2019 (T1) to October 2020 (T2) (p = 0.036). Conclusions: The low TEI scores in the pandemic cohort may be attributed to the sudden psychological and social effects of the pandemic. Moreover, with advancing age and years of medical curriculum, the TEI scores increased.
Keywords: emotional intelligence; medical education; medical students; pandemic; questionnaire.
Copyright © 2024, Bhat et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. School of Medical Sciences and Research issued approval (SU/SMS&R/76-A/2019/186). Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Benchmarking of Emotional Intelligence in radiography students within KwaZulu- Natal, South Africa.Radiography (Lond). 2022 May;28(2):487-491. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2021.10.017. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Radiography (Lond). 2022. PMID: 34742633
-
Hopelessness and burnout in Italian healthcare workers during COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of trait emotional intelligence.Front Psychol. 2023 May 5;14:1146408. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1146408. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37213395 Free PMC article.
-
Trait Emotional Intelligence and Self-regulated Learning in University Students during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediation role of Intolerance of Uncertainty and COVID-19 Perceived Stress.Pers Individ Dif. 2023 Mar;203:111999. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2022.111999. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Pers Individ Dif. 2023. PMID: 36415560 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Trait Emotional Intelligence in Academic Performance: Theoretical Overview and Empirical Update.J Psychol. 2016;150(2):229-51. doi: 10.1080/00223980.2015.1079161. Epub 2015 Oct 29. J Psychol. 2016. PMID: 26515326 Review.
-
Emotional intelligence education in pre-registration nursing programmes: an integrative review.Nurse Educ Today. 2015 Mar;35(3):510-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Nurse Educ Today. 2015. PMID: 25499529 Review.
References
-
- Learning objectives for medical student education-guidelines for medical schools: report I of the Medical School Objectives Project. Acad Med. 1999;74:13–18. - PubMed
-
- A longitudinal study of emotional intelligence training for otolaryngology residents and faculty. Dugan JW, Weatherly RA, Girod DA, Barber CE, Tsue TT. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;140:720–726. - PubMed
-
- A comprehensive meta-analysis of the relationship between emotional Intelligence and health. Martins A, Ramalho N, Morin E. Pers Individ Dif. 2010;49:554–564.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
