Path Analysis of Health Literacy, Social Support, and Self-Efficacy on Decisional Conflict in Patients with Stable Schizophrenia
- PMID: 39720413
- PMCID: PMC11668049
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S482994
Path Analysis of Health Literacy, Social Support, and Self-Efficacy on Decisional Conflict in Patients with Stable Schizophrenia
Abstract
Purpose: Constructing a multiple mediation model based on two mediating variables, social support and self-efficacy, to explore the mechanism of health literacy's effect on decisional conflict in patients with stable schizophrenia.
Patients and methods: A total of 205 patients with stable schizophrenia who were hospitalized in a psychiatric hospital in Guangdong Province, China, were selected for the study. The All Aspects of Health Literacy Scale (AAHLS), Decisional Conflict Scale (DCS), Social Support Rating Scale (SSRS) and General Self-Efficacy Scale (GSES) were used to evaluate health literacy, decisional conflict, social support and self-efficacy. Path analysis was performed by constructing a structural equation model, and the mediating effect between variables was validated by the bias-corrected nonparametric percentile bootstrap method.
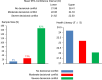
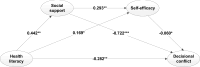
Results: Health literacy, social support, and self-efficacy together explained 20.4% of the variance in decisional conflict. (1) Severe decisional conflict group accounted for 82% of overall patients with stable schizophrenia. (2) there were strong and significant negative relationships between decisional conflict and health literacy, social support, self-efficacy and each of their dimensions (r=-0.14-0.27, P<0.01 or P<0.05). (3) The path analysis showed that health literacy directly affects decisional conflict (β=-0.282); additionally, health literacy indirectly affects decisional conflict through social support (β=-0.319), self-efficacy (β=-0.010) and through the chain mediating effect of social support and self-efficacy (β=-0.008).
Conclusion: Patients with stable schizophrenia have serious decisional conflict in China, and necessary interventions have to be made. This study found that social support and self-efficacy mediate the relationship between health literacy and decisional conflict in patients with stable schizophrenia in China. Healthcare professionals should emphasize health literacy education for patients, and implement pathway-based targeted interventions to improve health literacy, reduce decisional conflict, and promote the recovery of patients with stable schizophrenia.
Keywords: decisional conflict; health literacy; mediating role; stable schizophrenia; structural equation model.
© 2024 He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Path Analysis of Self-Efficacy, Coping Style and Resilience on Depression in Patients with Recurrent Schizophrenia.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Sep 1;19:1901-1910. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S421731. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 37680590 Free PMC article.
-
Structural equation modeling analysis of factors influencing decisional conflict between dialysis modality among end-stage kidney disease patients in Wuhan.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Oct 17;25(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03805-6. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39420277 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with Advance Care Planning Engagement Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Clin Nurs. 2024 Sep 20. doi: 10.1111/jocn.17458. Online ahead of print. J Clin Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39301973
-
The influence of health literacy, anxiety and education on shared decision making and decisional conflict in older adults, and the mediating role of patient participation: A video observational study.Patient Educ Couns. 2024 Jul;124:108274. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2024.108274. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Patient Educ Couns. 2024. PMID: 38547640
-
Chain Mediating Effect of Social Support and Trust in Physician on Stroke Caregivers' Decision Self-Efficacy and Decision Conflict.Nurs Health Sci. 2025 Mar;27(1):e70040. doi: 10.1111/nhs.70040. Nurs Health Sci. 2025. PMID: 39853695
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources