Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1, a brain tumor oncoprotein (Review)
- PMID: 39720461
- PMCID: PMC11667447
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2024.2810
Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1, a brain tumor oncoprotein (Review)
Abstract
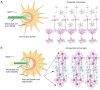
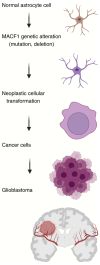
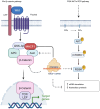
Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 (MACF1), is a cytoskeletal protein that functions as a crosslinker between microtubules and actin filaments, with early studies expanding the role of this spectraplakin protein to the central nervous system and Wnt signaling. In the early 2000's, genetic alterations of MACF1 were identified in several cancers suggesting that this cytoskeletal crosslinker was involved in tumor development and progression, while preclinical studies provided evidence that MACF1 is a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in glioblastomas, a central nervous system cancer derived from astrocytes and neural progenitor stem cells. Furthermore, investigations in glioblastomas demonstrated that genetic inhibitory targeting of this spectraplakin protein alone and in combination with DNA damaging agents had synergistic antitumorigenic effects. The established role of MACF1 in Wnt signaling, a known mechanistic driver of central nervous system development and pro-tumorigenic cell behavior in glioblastomas, provide a premise for addressing the potential of this spectraplakin protein as a novel oncoprotein in cancers with origins in the nervous system. The present review provides a summary of the role and function of MACF1 in the central nervous system, Wnt signaling and cancer development, specifically as an oncoprotein that underlie the transformation and oncogenic properties of glioblastomas.
Keywords: MACF1; Wnt; astrocytes; cancer; glioblastoma; nervous system; oncoprotein; tumor development.
Copyright: © 2024 Bonner and Quick.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
