Characteristics and Effectiveness of XP-Endo Files and Systems: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39720541
- PMCID: PMC11668552
- DOI: 10.1155/ijod/9412427
Characteristics and Effectiveness of XP-Endo Files and Systems: A Narrative Review
Abstract
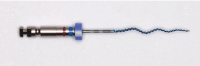
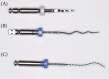
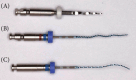
Background: XP-endo files are composed of Max-Wire alloy, which was developed by FKG Dentaire (La Chaux-de-Fonds, Switzerland). This alloy, known as Martensite-Austenite Electropolish Flex, is the first NiTi alloy used in endodontics to combine the shape memory effect with superelasticity for use in clinical practice. Objective: This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the existing knowledge and evidence regarding different XP-endo files and systems, XP-endo Finisher (XPEF), XP-endo Shaper (XPES), XP-endo Retreatment (XPER), XP-endo Rise (XPE-Rise), and XPE-Rise Retreatment (XPE-Rise-R), to help clinicians understand their different properties and recommended clinical uses. Moreover, this review aims to identify future research opportunities in this field. Materials and Methods: A search was performed in the PubMed database using the keywords "XP endo" or "XP-endo". A total of 309 studies were identified during the initial search, and then initial abstract screening was conducted. The inclusion criteria included any study that aimed to evaluate XP endo files and systems on permanent teeth, either in vivo or in vitro. We excluded studies that were unrelated to the subject, literature reviews, case studies, and studies that employed deciduous teeth. Finally, we performed an extensive review of the selected 130 studies, which we assessed, summarized, and classified based on the specific XP-endo file used. Conclusion: Overall, XP-endo files offer significant improvements in endodontic treatment. XPEF excels in irrigation activation and medicament removal, and XPES succeeds in canal cleaning, shaping, and retreatment. The XPER system, which incorporates the XPEF-R file, shows promise in removing root-filling materials, but its performance is inconsistent compared to other retreatment systems. We have found limited information regarding the latest XPE-Rise and XPE-Rise-R systems, additional research is required to fully determine their comparative effectiveness and optimize their clinical application.
Copyright © 2024 Sarah M. Alkahtany et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

