Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Cellular Immunity in Grades III-IV Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39720550
- PMCID: PMC11664745
- DOI: 10.22038/ABJS.2024.78412.3612
Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Cellular Immunity in Grades III-IV Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objectives: In this study, the Kellgren and Lawrence system was used as the most common radiographic grading system for diagnosis of osteoarthritis in patients defined as Grade III and IV. It is aimed to reveal oxidative stress and cellular immunity status. In this context, the aim is to discuss possible risk parameters regarding disease process and treatment effectiveness.
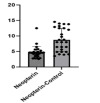
Methods: Twenty-five patients and 25 healthy individuals were included in the study. Total antioxidant, total oxidative stress, and thiol-disulfide balance values were determined spectrophotometrically in blood samples taken from individuals in the study groups. Neopterin levels were determined by the HPLC method.
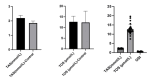
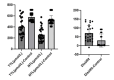
Results: In our study, total antioxidant status (TAS) values were found to be lower in the healthy control group than in the patient group (p=0.000). There was no statistically significant difference between the groups in total oxidant status (TOS) (p=0.815). The oxidative stress index (OSI) value evaluated based on TAS and TOS values did not show a statistical difference between the groups (p=0.065). The native thiol levels were determined to be statistically significantly lower in the patient group (p=0.000). But, disulfide and neopterin values were statistically significantly higher in the patient group (p=0.001 and p=0.000).
Conclusion: According to the findings of the current study; It is observed that the oxidant balance of individuals with osteoarthritis is disrupted in favor of free radicals, and as a result, cellular immunity decreases due to inflammation and the disease process. It is observed that these parameters change in direct proportion to the staging of the disease, especially in patients with stage III-IV knee osteoarthritis.
Keywords: Cellular immunity; Osteoarthritis; Oxidative stress.
© 2024 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Smith E, et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):819–828. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources