The potential role of n-3 fatty acids and their lipid mediators on asthmatic airway inflammation
- PMID: 39720728
- PMCID: PMC11666451
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1488570
The potential role of n-3 fatty acids and their lipid mediators on asthmatic airway inflammation
Abstract
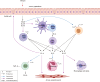
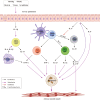
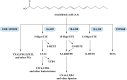
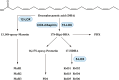
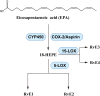
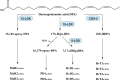
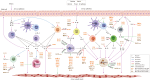
Asthma, is a common, significant and diverse condition marked by persistent airway inflammation, with a major impact on human health worldwide. The predisposing factors for asthma are complex and widespread. The beneficial effects of omega-3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in asthma have increasingly attracted attention recently. In asthma therapy, n-3 PUFAs may reduce asthma risk by controlling on levels of inflammatory cytokines and regulating recruitment of inflammatory cells in asthma. The specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) derived from n-3 PUFAs, including the E- and D-series resolvins, protectins, and maresins, were discovered in inflammatory exudates and their biosynthesis by lipoxygenase mediated pathways elucidated., SPMs alleviated T-helper (Th)1/Th17 and type 2 cytokine immune imbalance, and regulated macrophage polarization and recruitment of inflammatory cells in asthma via specific receptors such as formyl peptide receptor 2 (ALX/FPR2) and G protein-coupled receptor 32. In conclusion, the further study of n-3 PUFAs and their derived SPMs may lead to novel anti-inflammatory asthma treatments.
Keywords: asthma; inflammation; maresin; n-3 fatty acid; protectin; resolvin.
Copyright © 2024 Tian, Sun, Jiao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
Author D-MJ is employed by Shouyao Holdings Beijing Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E-series resolvin metabolome, biosynthesis and critical role of stereochemistry of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflammation-resolution: Preparing SPMs for long COVID-19, human clinical trials, and targeted precision nutrition.Semin Immunol. 2022 Jan;59:101597. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101597. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Semin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35227568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards targeting resolution pathways of airway inflammation in asthma.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jun;186:98-113. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Jan 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29352860 Review.
-
Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1851(4):469-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.010. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25149823 Review.
-
Role of omega-3 fatty acids and their metabolites in asthma and allergic diseases.Allergol Int. 2015 Jan;64(1):27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2014.08.003. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Allergol Int. 2015. PMID: 25572556 Review.
-
Proresolving lipid mediators resolvin D1, resolvin D2, and maresin 1 are critical in modulating T cell responses.Sci Transl Med. 2016 Aug 24;8(353):353ra111. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf7483. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27559094 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Urban Lifestyle and Climate-Driven Environmental Exposures: Immunological Consequences for Pediatric Respiratory Allergies.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025 Aug;13(8):e70248. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70248. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025. PMID: 40801216 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators . Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet (British edition). (2020) 396:1204–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

