IoT-based remote monitoring system: A new era for patient engagement
- PMID: 39720747
- PMCID: PMC11665796
- DOI: 10.1049/htl2.12089
IoT-based remote monitoring system: A new era for patient engagement
Abstract
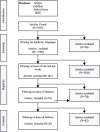
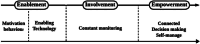
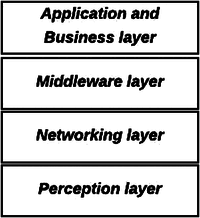
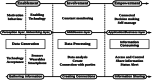
Internet of Things (IoT) is changing patient engagement in healthcare by shifting from traditional care models to a continuous, technology-driven approach using IoT-based Remote Monitoring Systems (IoT-RMS). This research seeks to redefine patient engagement by examining how Internet of Things (IoT) technologies can impact healthcare management and patient-provider interactions at different phases. Additionally, it presents the relationship between patient engagement stages and IoT-RMS, which promotes patients' active participation using technological health management tools. The study emphasizes that IoT-RMS improves patient engagement, organized into three main stages: enabling, engaging, and empowering. This approach shows how technological progress encourages patient involvement and empowerment, leading to improved health results and personalized care. A systematic review and narrative analysis of Web of Science (WOS), Scopus databases, IEEE, and PubMed yielded 1832 studies regarding patient engagement and technology. Despite the optimistic findings, the article highlights the need for more research to evaluate the durability of technology interventions and long-term effectiveness.
Keywords: Internet of Things; IoT‐remote monitoring system; patient engagement.
© 2024 The Author(s). Healthcare Technology Letters published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vincenzo, J.L. , Patton, S.K. , Lefler, L.L. , McElfish, P.A. , Wei, J. , Curran, G.M. : Older adults’ perceptions and recommendations regarding a falls prevention self‐management plan template based on the health belief model: A mixed‐methods study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19(4), 1–13 (2022) 10.3390/ijerph19041938 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

