Factors related to sedentary behavior in older adult stroke patients in China: a study based on decision tree and logistic regression model
- PMID: 39720807
- PMCID: PMC11666432
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1457151
Factors related to sedentary behavior in older adult stroke patients in China: a study based on decision tree and logistic regression model
Abstract
Objective: This study investigates the factors influencing sedentary behavior in older adult Chinese stroke patients using decision trees and logistic regression models.
Methods: Convenience sampling method was employed to enroll 346 respondents aged ≥60 years with stroke from the Department of Neurology of three tertiary-level A hospitals in Heilongjiang province, based on the inclusion criteria. The Sedentary Behavior Questionnaire for Older Adults, the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-S), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS), and the Social Support Scale (SSRS) were used to assess sedentary behavior, physical activity level, sleep quality, depressive symptoms, and social support, respectively. Decision tree and logistic regression models were employed to analyze the factors related to sedentary behavior in older adult stroke patients.
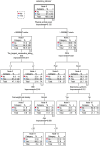
Results: Of the 346 respondents, 233 (67.3%) had sedentary behavior. The logistic regression model showed that education level (OR = 2.843, 95%CI: 1.219-6.626), BMI (OR = 3.686, 95%CI: 1.838-7.393), longest consecutive sitting time (OR = 3.853, 95%CI: 1.867-7.953), and sleep quality (OR = 3.832, 95%CI: 1.716-8.557) were identified as risk factors for sedentary behavior in older adult stroke patients, while drink alcohol (OR = 0.386, 95%CI: 0.184-0.809) and physical activity level (OR = 0.064, 95%CI: 0.030-0.140) were identified as protective factors for sedentary behavior. Besides, the decision tree model showed that physical activity level, longest consecutive sitting time, sleep quality, BMI, depressive symptoms, and age were associated with sedentary behavior. The sensitivity and specificity of the logistic regression model were 69.9 and 93.1%, respectively, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was 0.900 (95% CI: 0.863-0.938). The sensitivity and specificity of the decision tree model were 66.4, and 93.1% respectively, and the area under the ROC curve was 0.860 (95% CI: 0.816-0.904).
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that physical activity level, longest consecutive sitting time, sleep quality, and BMI were key factors associated with sedentary behavior. To achieve the purpose of improving rehabilitation effect and quality of life, this study combining decision trees with logistic regression models was of high value in studying factors influencing sedentary behavior in older adult stroke patients.
Keywords: cerebral apoplexy; decision tree; influencing factors; logistic regression model; older adult patients; sedentary behavior.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Li, Chen, Jiang, Tang and Lv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical