Dietary Carrageenan Amplifies the Inflammatory Profile, but not Permeability, of Intestinal Epithelial Cells from Patients With Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 39720875
- PMCID: PMC12069985
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izae306
Dietary Carrageenan Amplifies the Inflammatory Profile, but not Permeability, of Intestinal Epithelial Cells from Patients With Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Background: The consumption of ultra-processed foods has increased significantly worldwide and is associated with the rise in inflammatory bowel diseases. However, any causative factors and their underlying mechanisms are yet to be identified. This study aimed to further elucidate whether different types of the dietary emulsifier carrageenan (CGN) can alter the permeability and inflammatory state of the intestinal epithelium.
Methods: Caco-2/HT29-MTX cocultures (n = 4) were exposed to either κ-, ι-, or λ-CGN (100 µg mL-1) for 24 hours. Organoid-derived monolayers from patients with Crohn's Disease (CD) were exposed to κ-CGN (100 µg mL-1) for 48 hours (n = 10). In both models, an inflamed condition was established by adding a mix of inflammatory stimuli. Changes in permeability were measured by transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER). In the organoid-derived monolayers, cytokines were quantified in the apical and basolateral supernatant and gene expression was analyzed with RT-qPCR.
Results: None of the CGN subtypes altered permeability of non-inflamed or inflamed Caco-2/HT29-MTX cocultures. In organoid-derived monolayers, κ-CGN did not affect TEER, but induced alterations in the gene expression of tight junctions and mucus proteins. Expression of TNF, IL8, and IL1B increased upon κ-CGN stimulation, both in inflamed and non-inflamed monolayers. Cytokine release in the supernatant was increased by κ-CGN for IL-6, IL-13, IL-4, IL-2, and IL-10.
Conclusions: Dietary CGN caused upregulation of inflammatory markers and affected cytokine release of intestinal epithelial cells from CD patients, while permeability remained unaltered. When inflammation was already present, this pro-inflammatory effect was more pronounced, suggesting a role for dietary CGN during active CD.
Keywords: emulsifiers; inflammatory bowel diseases; intestinal epithelium; organoids; ultra-processed foods.
Plain language summary
This study revealed that the dietary emulsifier carrageenan has direct pro-inflammatory effects on intestinal epithelial cells from patients with Crohn’s disease, without affecting permeability. In an inflamed setting, this was more pronounced, suggesting a role for dietary carrageenan during active inflammation.
© 2024 Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
B.V. receives research support from AbbVie, Biora Therapeutics, Landos, Pfizer, Sossei Heptares and Takeda; receives speaker’s fees from Abbvie, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Chiesi, Falk, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, Lily, MSD, Pfizer, R-Biopharm, Sandoz, Takeda, Tillots Pharma, Truvion and Viatris; receives consultancy fees from Abbvie, Alfasigma, Alimentiv, Applied Strategic, Astrazeneca, Atheneum, BenevolentAI, Biora Therapeutics, Boxer Capital, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Guidepont, Landos, Lily, Merck, Mylan, Nxera, Inotrem, Ipsos, Janssen, Pfizer, Progenity, Sandoz, Sanofi, Santa Ana Bio, Sapphire Therapeutics, Sosei Heptares, Takeda, Tillots Pharma, and Viatris; stock options Vagustim. M.F. receives financial support for research from AbbVie, Biogen, EG, Janssen, Pfizer, Takeda, and Viatris; receives speakers’ fees from AbbVie, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Falk, Ferring, Janssen-Cilag, MSD, Pfizer, Takeda, Truvion Healthcare, and Viatris; and receives consultancy fees from AbbVie, Agomab Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, MRM Health, MSD, Pfizer, Takeda, and Thermo Fisher. S.V. receives financial support for research from AbbVie, J&J, Pfizer, Takeda, and Galapagos; receives speakers’ and consultancy fees from AbbVie, Abivax, AbolerIS Pharma, AgomAb, Alimentiv, Arena Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Cytoki Pharma, Dr Falk Pharma, Ferring, Galapagos, Genentech-Roche, Gilead, GSK, Hospira, Imidomics, Janssen, J&J, Lilly, Materia Prima, Mestag Therapeutics, MiroBio, Morphic, MrMHealth, Mundipharma, MSD, Pfizer, Prodigest, Progenity, Prometheus, Robarts Clinical Trials, Surrozen, Takeda, Theravance, Tillots Pharma AG, VectivBio, Ventyx, Zealand Pharma. C.M. is chair of the KU Leuven Fund “Nutrition,” a donation-based fund to stimulate research on nutrition. Recipient of travel/accommodation expenses and small participation fee (< 100€/meeting) as a member of working groups of the Belgian Superior Health Council and Belgian Federal Agency of the Safety of the Food Chain. Recipient of travel/accommodation expenses as member of the scientific advisory body of the EU Joint Programme Initiative Healthy Diet, Healthy Life, as co-chair ILSI Europe Task Force Dietary Intake and Exposure, as member ILSI Europe Task Force Nutrient Intake Optimisation. Recipient of honoraria (< 500€/year) as an active member of the advisory board of NutriNews (Belgian Nutrition Information Center). Recipient of honoraria as jury-member of nutrition-related awards and reviewing EU-grants. Recipient of royalties form a textbook (Handboek Voeding, ACCO). Honoraria are used to support research of PhD Students. J.S. receives financial support for research from Galapagos and Viatris; receives speakers’ fees from Abbvie, Falk, Takeda, Pfizer, Galapagos, Ferring, Janssen, and Fresenius; and does consultancy for Janssen, Ferring, Fresenius, Abbvie, Galapagos, Celltrion, Pharmacosmos, and Pharmanovia. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

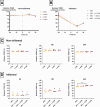
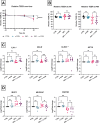
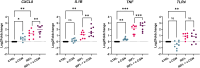
References
-
- Tahiri M, Johnsrud C, Steffensen IL.. Evidence and hypotheses on adverse effects of the food additives carrageenan (E 407)/processed Eucheuma seaweed (E 407a) and carboxymethylcellulose (E 466) on the intestines: a scoping review. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2023;53(9):521-571. doi: https://doi.org/ 10.1080/10408444.2023.2270574 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Winter CA, Risley EA, Nuss GW.. Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for antiinflammatory drugs. Exp Biol Med. 1962;111(3):544-547. doi: https://doi.org/ 10.3181/00379727-111-27849 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Watt J, Marcus R.. Experimental ulcerative disease of the colon in animals. Gut. 1973;14(6):506-510. doi: https://doi.org/ 10.1136/gut.14.6.506 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weiner ML. Food additive carrageenan: Part II: a critical review of carrageenan in vivo safety studies. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014;44(3):244-269. doi: https://doi.org/ 10.3109/10408444.2013.861798 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

