Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improved Neovascularisation Following Limb Ischaemia-The Role of ROS Mitigation
- PMID: 39720917
- PMCID: PMC11669187
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70310
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improved Neovascularisation Following Limb Ischaemia-The Role of ROS Mitigation
Abstract
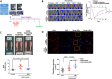
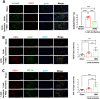
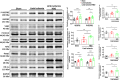
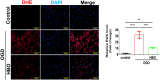
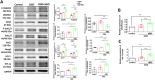
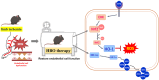
Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy has emerged as a potential treatment, shown to enhance blood flow and angiogenesis. However, specific effects and mechanisms of HBO on limb ischaemia responding to a hypoxic environment remain largely unknown. We aimed to investigate the therapeutic potential of HBO in the treatment of limb ischaemia. Following limb ischaemia surgery, we evaluated the angiogenic capacity in wild-type C57BL/6J mice subjected to HBO treatment (100% oxygen at 3 ATA for 1 h/day for five consecutive days) compared to untreated controls. Notably, through laser Doppler perfusion imaging and CD31 staining mice receiving HBO postlimb ischaemia surgery exhibited significantly enhanced angiogenic capability and reduced ROS expression compared to nontreated counterparts. Additionally, in vitro experiments were conducted to investigate whether HBO could mitigate endothelial cell dysfunction and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production triggered by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). HBO treatment rescued the impaired proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial cells following OGD. Mechanistically, HBO upregulated the expression of proangiogenic proteins, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), haem oxygenase-1 (HO-1), hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Collectively, HBO treatment shows promise in augmenting the endogenous angiogenic potential and suppressing ROS levels in limb ischaemia.
Keywords: HBO; ROS; angiogenesis; limb ischaemia.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuated limb ischemia in mice with high-fat diet by restoring Sirtuin 1 and mitochondrial function.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Mar 16;230:263-272. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.01.056. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39956474
-
VEGF and bFGF induction by nitric oxide is associated with hyperbaric oxygen-induced angiogenesis and muscle regeneration.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 17;10(1):2744. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59615-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32066777 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of osteoglycin promotes angiogenesis in limb ischaemia mouse models via modulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 signalling pathway.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Jan;113(1):70-80. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw220. Epub 2016 Oct 23. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28069703
-
Hyperbaric oxygen potentiates diabetic wound healing by promoting fibroblast cell proliferation and endothelial cell angiogenesis.Life Sci. 2020 Oct 15;259:118246. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118246. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32791151
-
Circulatory Rejuvenated EPCs Derived from PAOD Patients Treated by CD34+ Cells and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Salvaged the Nude Mouse Limb against Critical Ischemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 23;21(21):7887. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217887. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33114267 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

