Thin flap sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty in patellar instability yields good functional outcomes without progressive cartilage deterioration in the short-term follow-up-A retrospective single-surgeon cohort study
- PMID: 39720939
- PMCID: PMC12392387
- DOI: 10.1002/ksa.12566
Thin flap sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty in patellar instability yields good functional outcomes without progressive cartilage deterioration in the short-term follow-up-A retrospective single-surgeon cohort study
Abstract
Purpose: Sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty (TP) effectively treats patellofemoral (PF) instability (PFI) caused by high-grade trochlear dysplasia (TD), but current evidence is based on small case series. We hypothesised, that TP would result in significant functional improvements and a low re-dislocation rate but would not accelerate the progression of PF cartilage deterioration.
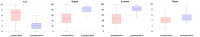
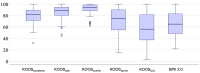
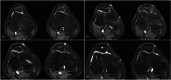
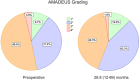
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all TP cases performed by a single surgeon between 2015 and 2021. Inclusion criteria were postoperative Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) >6 and >12 months and a clinical follow-up >12 months. Patients with simultaneous cartilage repair, open physes or incomplete records were excluded. Clinical outcomes were assessed using pre- and postoperative scores, postoperative Banff Patellofemoral Instability Instrument (BPII) 2.0 and Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS), re-dislocation rate and patient satisfaction. PF cartilage was evaluated via Area Measurement and Depth & Underlying Structures (AMADEUS) scores preoperatively, at 6 months and at the final follow-up.
Results: We included 113 patients (25.8 ± 8.3 years) with high-grade TD (Dejour B-D; mean lateral inclination angle: -2.9 ± 9.1°), 85% of whom had advanced cartilage lesions. All underwent TP, lateral retinacular lengthening (LRL) and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction (MPFL-R). After 34.8 ± 20.9 months, function, pain levels and Tegner scores improved significantly (p < 0.001). KOOS dimensions were: symptoms 79.9 ± 13.5, pain 86.4 ± 12.1, activity 91.9 ± 8.3, sports 71.7 ± 22.2 and quality-of-life 58.1 ± 23.8. BPII 2.0 was 64.3 ± 31.4. Preoperative AMADEUS scores (55.2 ± 17.4) remained stable at 6 months (p = 0.343) but improved to 58.4 ± 16.0 at 28.6 (12-89) months (p = 0.004). Complication and re-dislocation rates were 5.3% and 1.8%, with 93% patient satisfaction.
Conclusion: Sulcus-deepening TP with MPFL-R and LRL yields good to excellent short-term results without progressive chondral deterioration, enabling patients to return to their prior or higher activity levels despite advanced preoperative chondral lesions. TP can be considered a safe, joint-preserving technique for PF stabilisation.
Level of evidence: Level III, retrospective cohort study.
Keywords: cartilage deterioration; maltracking; patellofemoral instability; trochlear dysplasia; trochleoplasty.
© 2024 The Author(s). Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Karl‐Heinz Frosch receives royalties from Arthrex (Naples, FL, USA). Karl‐Heinz Frosch and Matthias Krause receive honoraria for lectures from Arthrex (Naples, FL, USA). Andreas Weiler receives royalties from Medacta International (Castel San Pietro, Switzerland) and honoraria for lectures from Enovis (Freiburg, Germany). Arno Schmeling receives payments from a consulting contract with Arthrex (Naples, FL, USA) and honoraria for presentations from Conmed (Utica, NY, USA). He is head of the Patellofemoral Committee of the German Society for Knee Surgery. Jannik Frings and Eva Janssen declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Askenberger, M. , Janarv, P.M. , Finnbogason, T. & Arendt, E.A. (2017) Morphology and anatomic patellar instability risk factors in first‐time traumatic lateral patellar dislocations: a prospective magnetic resonance imaging study in skeletally immature children. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 45, 50–58. Available from: 10.1177/0363546516663498 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balcarek, P. , Ammon, J. , Frosch, S. , Walde, T.A. , Schüttrumpf, J.P. , Ferlemann, K.G. et al. (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of the medial patellofemoral ligament lesion in acute lateral patellar dislocations considering trochlear dysplasia, patella alta, and tibial tuberosity‐trochlear groove distance. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery, 26, 926–935. Available from: 10.1016/j.arthro.2009.11.004 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

