Application of large language models in disease diagnosis and treatment
- PMID: 39722188
- PMCID: PMC11745858
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003456
Application of large language models in disease diagnosis and treatment
Abstract
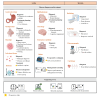
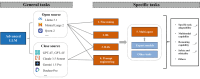
Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Claude, Llama, and Qwen are emerging as transformative technologies for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. With their exceptional long-context reasoning capabilities, LLMs are proficient in clinically relevant tasks, particularly in medical text analysis and interactive dialogue. They can enhance diagnostic accuracy by processing vast amounts of patient data and medical literature and have demonstrated their utility in diagnosing common diseases and facilitating the identification of rare diseases by recognizing subtle patterns in symptoms and test results. Building on their image-recognition abilities, multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) show promising potential for diagnosis based on radiography, chest computed tomography (CT), electrocardiography (ECG), and common pathological images. These models can also assist in treatment planning by suggesting evidence-based interventions and improving clinical decision support systems through integrated analysis of patient records. Despite these promising developments, significant challenges persist regarding the use of LLMs in medicine, including concerns regarding algorithmic bias, the potential for hallucinations, and the need for rigorous clinical validation. Ethical considerations also underscore the importance of maintaining the function of supervision in clinical practice. This paper highlights the rapid advancements in research on the diagnostic and therapeutic applications of LLMs across different medical disciplines and emphasizes the importance of policymaking, ethical supervision, and multidisciplinary collaboration in promoting more effective and safer clinical applications of LLMs. Future directions include the integration of proprietary clinical knowledge, the investigation of open-source and customized models, and the evaluation of real-time effects in clinical diagnosis and treatment practices.
Copyright © 2024 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating text and visual diagnostic capabilities of large language models on questions related to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Atlas 5th edition.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025 Mar 3;31(2):111-129. doi: 10.4274/dir.2024.242876. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39248152 Free PMC article.
-
Large Language Models in Medicine: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions.Int J Med Sci. 2025 May 31;22(11):2792-2801. doi: 10.7150/ijms.111780. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal LLMs for retinal disease diagnosis via OCT: few-shot versus single-shot learning.Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2025 May 20;17:25158414251340569. doi: 10.1177/25158414251340569. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40400723 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Breast Imaging Today and in the Near Future.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 May 4. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29807. Online ahead of print. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40320742 Review.
-
Large language models and psychiatry.Int J Law Psychiatry. 2025 Jul-Aug;101:102086. doi: 10.1016/j.ijlp.2025.102086. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40020592
Cited by
-
Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Applications: A Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jun 10;12(6):631. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12060631. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of large language models in generating pulmonary nodule follow-up recommendations.Eur J Radiol Open. 2025 Apr 30;14:100655. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2025.100655. eCollection 2025 Jun. Eur J Radiol Open. 2025. PMID: 40391069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varghese J, Chapiro J. ChatGPT: The transformative influence of generative AI on science and healthcare. J Hepatol 2024;80:977–980. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.028. - PubMed
-
- Raiaan MAK Mukta MSH Fatema K Fahad NM Sakib S Mim MMJ, et al. . A review on large language models: Architectures, applications, taxonomies, open issues and challenges. IEEE Access 2024;12:26839–26874. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3365742.
-
- Wei C, Wang YC, Wang B, Kuo CCJ. An overview of language models: Recent developments and outlook. APSIPA Trans Signal Inf Process 2024;13. doi: 10.1561/116.00000010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

