Public awareness, knowledge, and attitude toward epilepsy in Lebanon: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39722692
- PMCID: PMC11668639
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1480960
Public awareness, knowledge, and attitude toward epilepsy in Lebanon: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Purpose: Epilepsy, a prevalent chronic neurological disorder, is associated with misconceptions, negative attitudes, and stigma because of poor public knowledge and awareness. Therefore, the purpose of the current study was to assess the knowledge, awareness, and attitudes toward epilepsy and its associated factors among the Lebanese general population.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on Lebanese adults between October 2021 and June 2022 using an electronic structured self-administered questionnaire that was circulated online using the different social media platforms. Data related to participants' demographic characteristics, knowledge, awareness, and attitude about epilepsy were measured. Eight items were included in the knowledge score that ranged between "0 and 16", five items were included in the awareness score and ranged between 0 and 10. Likewise, the attitude score was calculated from 14 items and the score ranged between "0 and 28". Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, and logistic regression was employed to identify factors associated with knowledge and awareness of epilepsy.
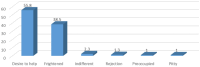
Results: A total of 301 participants filled the questionnaire with a mean age of 28.68 and majority (66%) were females. The analyzed scores revealed that most of the participants (87.4%) had a good knowledge regarding epilepsy as a disease with mean of 10.2 (± 2.14), 70.1% had good awareness about epilepsy with mean of 6.3 (± 1.4), and 88% had good attitude toward patients with epilepsy with mean of 21.5 (± 6.2). Attending lecture about epilepsy was significantly associated with higher knowledge (OR 5.756, CI 95% 4.652-11.676, p < 0.001), better awareness (OR 4.936, CI 95% 3.062-10.566, p < 0.001) and attitude (OR 5.187, CI 95% 1.687-9.761, p < 0.014) toward the disease.
Conclusion: The findings of this study reflected an adequate knowledge and awareness, as well a positive attitude toward patients with epilepsy in Lebanon. However, there is a need for raising societal awareness and understanding of epilepsy to minimize the public misconceptions and reduce the stigma and discriminatory attitudes toward epileptic patients.
Keywords: Lebanon; attitudes; awareness; epilepsy; knowledge; public.
Copyright © 2024 Younes, Chahine, Hanna, Mourad, Al Souheil, Al Mazrouei, Rahal and Malaeb.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources