Acceptance of COVID-19 vaccine and its related determinants in Nigeria: An online survey
- PMID: 39722760
- PMCID: PMC11551692
- DOI: 10.5501/wjv.v13.i4.98551
Acceptance of COVID-19 vaccine and its related determinants in Nigeria: An online survey
Abstract
Background: Vaccine hesitancy is a major challenge in the fight against the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Identifying the sociodemographic factors associated with vaccine acceptance among Nigerians is crucial for improving vaccine uptake.
Aim: To assess the acceptance rate of COVID-19 vaccine and its related determinants among Nigerians.
Methods: An online cross-sectional survey (observational study) was conducted between February 2021 and May 2021, using a questionnaire hosted on SurveyMonkey. The invitation to take part in the poll was sent out to participants through social networking platforms. A logistic regression was used to determine which sociodemographic factors were associated with vaccine acceptance constructs.
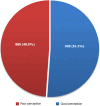
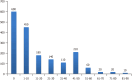
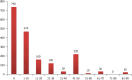
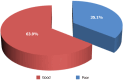
Results: A total of 1800 persons responded to the survey, a larger proportion of whom were males (53.9%) and within the age group of 21-30 years (29.4%) and earned an average income of less than $500 per month (43.3%). Only 0.56% of participants had a high perceived risk of COVID-19 infection, while only 1.11% had a perceived risk of dying from COVID-19. The perception rate of the COVID-19 vaccine among participants was 51.1%, while the acceptance rate was 63.9%. There was no significant association between the COVID-19 vaccine acceptance rate and related determinants assessed, particularly age (χ² = 3.049, P = 0.550), sex (χ² = 0.102, P = 0.749), average income (χ² = 3.802, P = 0.875), and religion (χ² = 2.819, P = 0.420). Participants with chronic conditions demonstrated a higher acceptance rate compared to the general population.
Conclusion: Despite the positive perception observed and substantial vaccine acceptance rate among the study participants, more public health interventions are still needed to enhance vaccine acceptability in Nigeria.
Keywords: Acceptance; COVID-19; Determinants; Hesitancy; Nigerians; Online survey; Vaccine.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determinants for Acceptance of COVID-19 Vaccine in Nigeria.Cureus. 2021 Nov 22;13(11):e19801. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19801. eCollection 2021 Nov. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34963828 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance in Saudi Arabia: A Web-Based National Survey.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020 Nov 20;13:1657-1663. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S276771. eCollection 2020. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020. PMID: 33262600 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance Among the General Adult Population in Saudi Arabia Based on the Health Belief Model: A Web-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2022 Aug 23;14(8):e28326. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28326. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36168376 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge about, attitude and acceptance towards, and predictors of intention to receive the COVID-19 vaccine among cancer patients in Eastern China: A cross-sectional survey.J Integr Med. 2022 Jan;20(1):34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2021.10.004. Epub 2021 Oct 26. J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 34774463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid review of evidence on the determinants of and strategies for COVID-19 vaccine acceptance in low- and middle-income countries.J Glob Health. 2021 Nov 20;11:05027. doi: 10.7189/jogh.11.05027. eCollection 2021. J Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34912550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

