MMPred: a tool to predict peptide mimicry events in MHC class II recognition
- PMID: 39722794
- PMCID: PMC11669352
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1500684
MMPred: a tool to predict peptide mimicry events in MHC class II recognition
Abstract
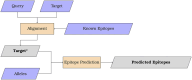
We present MMPred, a software tool that integrates epitope prediction and sequence alignment algorithms to streamline the computational analysis of molecular mimicry events in autoimmune diseases. Starting with two protein or peptide sets (e.g., from human and SARS-CoV-2), MMPred facilitates the generation, investigation, and testing of mimicry hypotheses by providing epitope predictions specifically for MHC class II alleles, which are frequently implicated in autoimmunity. However, the tool is easily extendable to MHC class I predictions by incorporating pre-trained models from CNN-PepPred and NetMHCpan. To evaluate MMPred's ability to produce biologically meaningful insights, we conducted a comprehensive assessment involving i) predicting associations between known HLA class II human autoepitopes and microbial-peptide mimicry, ii) interpreting these predictions within a systems biology framework to identify potential functional links between the predicted autoantigens and pathophysiological pathways related to autoimmune diseases, and iii) analyzing illustrative cases in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection and autoimmunity. MMPred code and user guide are made freely available at https://github.com/ComputBiol-IBB/MMPRED.
Keywords: MHC class II; SARS-CoV-2; autoimmune disease; epitope prediction; molecular mimicry; sequence alignment.
Copyright © 2024 Guerri, Junet, Farrés and Daura.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors FG, VJ and JF are employed by Anaxomics Biotech, Barcelona, Spain. The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abadi M., Agarwal A., Barham P., Brevdo E., Chen Z., Citro C., et al. (2016). TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv, 1603. 10.48550/arXiv.1603.04467 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

