Red cell distribution width to albumin ratio is associated with asthma risk: a population-based study
- PMID: 39722824
- PMCID: PMC11668568
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1493463
Red cell distribution width to albumin ratio is associated with asthma risk: a population-based study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Red cell distribution width to albumin ratio is associated with asthma risk: a population-based study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 18;12:1571811. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1571811. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40041462 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The red cell distribution width to albumin ratio (RAR), a newly identified biomarker of inflammation, has been linked to a variety of inflammatory diseases. Asthma, a major burden on global health, is an inflammatory airway disease that is profoundly affected by inflammation. This study primarily sought to examine the influence of RAR on the risk of developing asthma.
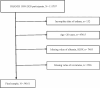
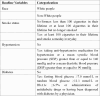
Methods: Data from 1999 to 2020 was gathered from the NHANES database. The impact of RAR on asthma risk and their non-linear relationship were clarified by multivariate logit and restricted cubic spline (RCS) analyses. Subgroup and interaction analyses collectively formed the sensitivity analysis for this study.
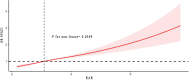
Results: This study was based on an analysis of 54,161 individuals. RAR has been identified as an independent risk factor for asthma, according to logit analysis. The moderate and high RAR groups had a 16% [95% confidence interval (CI): 1.06-1.27] and 43% (95% CI: 1.30-1.58) higher risk, respectively, compared to the lowest group. Every 0.5 unit increase in RAR almost doubled the risk of asthma [odds ratio (OR): 1.82, 95% CI: 1.55-2.12]. There was no non-linear relationship between RAR and asthma risk, based on RCS analysis. Combining subgroup and interaction analyses results, all subgroups in this study showed consistent trends with the overall population.
Conclusion: Notably, this article, the first to examine the relationship between RAR and asthma risk, unveiled a positive linear correlation between them. With an increase in RAR, whether analyzed as a categorical or continuous variable, asthma risk significantly increases. This finding was beneficial for clinicians to anticipate and assess the onset of asthma through stratified or dynamic management. Given RAR's numerous advantages, its application in clinical settings held considerable promise.
Keywords: NHANES; asthma; inflammation; red cell distribution width to albumin ratio; risk.
Copyright © 2024 Ding, Zhang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between red blood cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio and risk of depression: A cross-sectional analysis of NHANES.J Affect Disord. 2025 Jun 15;379:250-257. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2025.03.037. Epub 2025 Mar 12. J Affect Disord. 2025. PMID: 40086477
-
Association between red cell distribution width/serum albumin ratio and Parkinson's disease.Eur J Med Res. 2025 May 31;30(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02707-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40448230 Free PMC article.
-
Association between red blood cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio and prognosis in post-cardiac arrest patients: data from the MIMIC-IV database.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jan 7;11:1499324. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1499324. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 39839831 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Value of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-to-Albumin Ratio (RAR) in Predicting Mortality and Severity in Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Mar 27;17(3):e81279. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81279. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40291314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinobenzoic acids and nuclear retinoic acid receptors.Cell Struct Funct. 1991 Apr;16(2):113-23. doi: 10.1247/csf.16.113. Cell Struct Funct. 1991. PMID: 1650290 Review.
Cited by
-
Red cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio and hypertension risk: age-specific threshold effects identified in the 2017-2020 NHANES U.S. Adult population.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Aug 9;25(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-05072-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40783688 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation between red blood cell distribution width to serum albumin ratio and all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a retrospective study using the MIMIC-IV database.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 24;12:1604615. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1604615. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40630492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lan W, Liu E, Sun D, Li W, Zhu J, Zhou J, et al. Red cell distribution in critically ill patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulmonology. (2024) 30:34–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

