Influence of acupuncture intensity on analgesic effects in AA rat models
- PMID: 39723129
- PMCID: PMC11668573
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1502535
Influence of acupuncture intensity on analgesic effects in AA rat models
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the influence of acupuncture lifting-thrusting frequency and amplitude on the analgesic effects, and its correlation with mast cell degranulation.
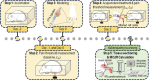
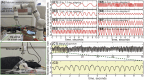
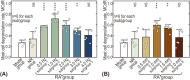
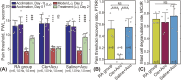
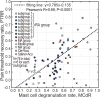
Methods: Acute adjuvant arthritis (AA) rat models were employed. Robot-arm aided lifting-thrusting acupuncture therapy was conducted with various frequencies (ranging from 0.5 to 4 Hz) and amplitudes (ranging from 0.5 to 2.0 mm). The rats' pain thresholds were measured multiple times before and after the therapy, and the analgesic effects were evaluated using the pain threshold recovery rate (PTRR), a normalized index. The mast cell degranulation rate (MCdR) at the acupoint was calculated, and a correlation analysis between PTRR and MCdR was performed.
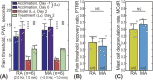
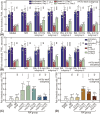
Results: Acupuncture therapy partially restored the pain threshold affected by arthritis. The analgesic effects were influenced by stimulus frequency and amplitude, with best outcomes occurring at an intermediate optimal frequency of 1.0 Hz and amplitude of 1.0-1.5 mm. Similarly, the MCdR peaked at the optimal frequency and amplitude.
Conclusion: Our animal experiment suggests that optimal analgesic effects can be achieved with stimulation at an optimal intensity. This intensity-effect correlation appears to originate from mast cell activation rates under different mechanical stimulus.
Keywords: acupuncture intensity; adjuvant arthritis; analgesia; mast cell; robot arm.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Liu, Zhang, Qiao, Li, Ren, Ding, Yao and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brzezińska-Błaszczyk E. (2011). Mast cells as a source and target for histamine in Biomedical aspects of histamine: current perspectives. Editors Khardori N., Ali Khan R., Tripathi T. (Springer; ), 247–284.
-
- Dimitrov N., Atanasova D., Tomov N., Sivrev D., Lazarov N. (2017). Acupuncture causes serotonin release by mast cells. Romanian J. Morphol. Embryology 58 (3), 961–968. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

