Improvement of silage characteristics of Lactobacillus salivarius HMC4 and improvement of silage quality of king grass
- PMID: 39723146
- PMCID: PMC11668806
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1468577
Improvement of silage characteristics of Lactobacillus salivarius HMC4 and improvement of silage quality of king grass
Abstract
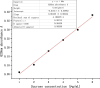
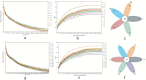
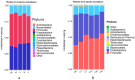
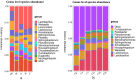
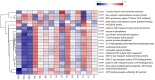
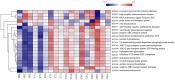
The effect of HMC4 produced by protoplast fusion on silage was studied. The silage formula was composed of heterozygote HMC4 (Group C), parent Lactobacillus (Group A) and a combination of two parents (Group B). The fermentation quality and microbial composition of each batch of silage were evaluated. The results showed that the propionic acid concentration in group C was the lowest, but the organic acid content in feed was significantly increased. Groups B and C had slightly lower crude fiber levels than group A, while groups A and C had higher levels of soluble sugars. The dynamic observation of C group showed that the nutrient composition of feed changed gradually with the extension of silage period. High-throughput sequencing revealed fluctuations in microbial composition before and after silage. Over time, Lactobacillus became the dominant strain and its numbers steadily increased.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; high-throughput sequencing; microbial communities; protoplast fusion; silage.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Zhao, Zhi, Lu, Qiao, Liu, Dou, Tan and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cardona E., Rios J., Peña J., Peñuela M., Rios L. (2016). King grass: a very promising material for the production of second generation ethanol in tropical countries. Biomass Bioenergy 95, 206–213. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.10.008 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

