FA-PEG Modified ZIF(Mn) Nanoparticles Loaded with Baicalin for Imaging-Guided Treatment of Melanoma in Mice
- PMID: 39723175
- PMCID: PMC11669047
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S493185
FA-PEG Modified ZIF(Mn) Nanoparticles Loaded with Baicalin for Imaging-Guided Treatment of Melanoma in Mice
Abstract
Background: Melanoma is an aggressive skin tumor with limited therapeutic options due to rapid proliferation, early metastasis, and poor prognosis. Baicalin (BA), a natural flavonoid, shows promise in inducing ferroptosis and apoptosis but faces challenges of poor solubility and bioavailability. To address these issues, we developed a multifunctional drug delivery system: manganese-doped ZIF-8 nanoparticles (ZIF(Mn)) loaded with BA and modified with folic acid (FA) and polyethylene glycol (PEG). FA targets melanoma cells by exploiting folate receptor overexpression, while PEG enhances biocompatibility and systemic circulation. Manganese enables magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for real-time, non-invasive therapy monitoring.
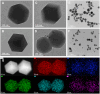
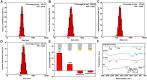
Methods: BA-loaded ZIF(Mn)/FA-PEG nanoparticles were synthesized via a one-pot method, enabling drug encapsulation, Mn²+ incorporation, and surface modification. The nanoparticles were comprehensively characterized (particle size, Zeta potential, FTIR, and XRD). Cytotoxicity and cellular uptake were evaluated in B16-F10 melanoma cells, and in vivo experiments in C57BL/6J mice investigated MR imaging capability, antitumor efficacy, and biosafety.
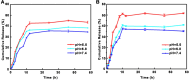
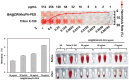
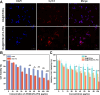
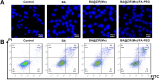
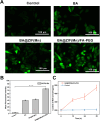
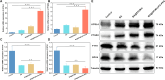
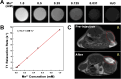
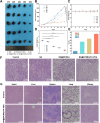
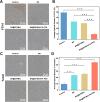
Results: BA@ZIF(Mn)/FA-PEG nanoparticles demonstrated excellent stability, a BA loading capacity of 33.50 ± 0.04%, and pH-responsive release, with accelerated drug release under acidic tumor conditions. Mn²+ provided strong T1-weighted MR imaging contrast. Cellular and animal studies showed enhanced uptake, reduced premature drug release, and improved compatibility. Mechanistically, the nanoparticles induced significant ferroptosis and apoptosis in melanoma cells, leading to potent antitumor effects.
Conclusion: The BA@ZIF(Mn)/FA-PEG nanoplatform effectively integrates targeted delivery, imaging guidance, and dual ferroptosis-apoptosis induction, offering a promising strategy for improving melanoma treatment outcomes.
Keywords: Baicalin; ferroptosis; folic acid targeted; magnetic resonance imaging; melanoma; metal−organic frameworks.
© 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preparation and evaluation of Baicalin-loaded albumin nanoparticles for anti-breast cancer activity.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jul;318(Pt 1):144799. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.144799. Epub 2025 Jun 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40460958
-
Folate-targeted pH-sensitive albumin nanoparticles loaded with Baicalin enhance tamoxifen efficacy in estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jul;318(Pt 3):145155. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145155. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40505927
-
Folic Acid Decorated Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF-8) Loaded with Baicalin as a Nano-Drug Delivery System for Breast Cancer Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 24;16:8337-8352. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S340764. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34992370 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalized ZIF-8 as a versatile platform for drug delivery and cancer therapy: strategies, challenges and prospects.J Mater Chem B. 2025 Mar 20;13(12):3758-3785. doi: 10.1039/d4tb02289k. J Mater Chem B. 2025. PMID: 40019146 Review.
-
Harnessing Folate Receptors: A Comprehensive Review on the Applications of Folate-Adorned Nanocarriers for the Management of Melanoma.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 May 19;8(5):3623-3656. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00077. Epub 2025 Apr 24. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 40275606 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomaterials for targeted drug delivery for immunotherapy of digestive tract tumors.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 5;16:1562766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1562766. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40109337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

