Resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid supplementation promotes ileal development and digestive function by altering microbial community abundance and metabolites in Tibetan sheep
- PMID: 39723186
- PMCID: PMC11668758
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1470992
Resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid supplementation promotes ileal development and digestive function by altering microbial community abundance and metabolites in Tibetan sheep
Abstract
Introduction: The effects of resveratrol (RES) and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid (HMB) on phenotype, immunity, digestive enzyme activity and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) contents in ileum of Tibetan sheep were investigated.
Methods: A total of 120 two-month-old Tibetan sheep (15.5 ± 0.14 kg) were randomly allocated to 4 treatments: control group (basal diet), RES group (basal diet +1.5 g RES/d), HMB group (basal diet +1.25 g HMB/d), RES-HMB group (basal diet +1.5 g RES/d + 1.25 g HMB/d).
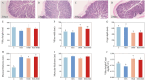
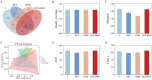
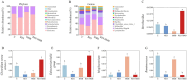
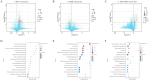
Results: Results indicated that dietary RES and (or) HMB supplementation significantly improved the phenotype (mucosal thickness and villus width), SCFAs concentrations, and digestive enzymes (lipase, cellulase, and α-amylase) (p < 0.05). The relative abundance of Brevibacillus, Clostridium sensu stricto 3, and Eubacterium hallii group were increased, while the abundance of Ruminococcus and Mogibacterium were decreased (p < 0.05) in the RES-HMB group. The metabolic profiling indicated an increase in the differential metabolites (DMs) including L-arginine, butanoic acid, D-mannose, and retinol were increased in the RES-HMB group (p < 0.05).
Discussion: In summary, our results suggested that RES and (or) HMB supplementation improved SCFAs concentration by up-regulating the microbial community abundance (Brevibacillus, Clostridium sensu stricto 3, and Eubacterium hallii group) and metabolism (L-arginine, butanoic acid, D-mannose, and retinol), thus contributing to ileal morphology and digestive enzyme activity. These findings may provides a novel reference for the nutritional regulation to improve the production of Tibetan sheep.
Keywords: Tibetan sheep; ileum; metabolite; microorganism; resveratrol; β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid.
Copyright © 2024 Gan, Ji, Su, Hou and Gui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of resveratrol and β-Hydroxy-β-methyl butyric acid supplementation alone or in combination on the development and health of the duodenum in Tibetan sheep.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1612102. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1612102. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40698187 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the effects of resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid under different protein levels on the ileal health of tibetan sheep.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1612170. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1612170. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40761281 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and metabolomic insights into the synergistic effects of resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid on hepatic function under varying protein diets in Tibetan sheep.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 8;12:1614114. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1614114. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40697554 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omics Revealed Resveratrol and β-Hydroxy-β-methyl Butyric Acid Alone or in Combination Improved the Jejunal Function in Tibetan Sheep.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;13(8):892. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080892. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199138 Free PMC article.
-
International society of sports nutrition position stand: β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB).J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025 Dec;22(1):2434734. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2024.2434734. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39699070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of resveratrol and β-Hydroxy-β-methyl butyric acid supplementation alone or in combination on the development and health of the duodenum in Tibetan sheep.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1612102. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1612102. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40698187 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the effects of resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid under different protein levels on the ileal health of tibetan sheep.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1612170. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1612170. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40761281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu Z, Zhang F, Su Q, Ji Q, Zhu K, Zhang Y, et al. . Integrating 16S rRNA sequencing and LC-MS-based metabolomics to evaluate the effects of dietary crude protein on ruminal morphology, fermentation parameter and digestive enzyme activity in Tibetan sheep. Animals. (2024) 14:2149. doi: 10.3390/ani14152149, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang FX, Sha YZ, He YY, Liu X, Chen XW, Yang WX, et al. . Age differences in ileum microbiota density: VFAs and their transport-related gene interactions in Tibetan sheep. Fermentation-Basel. (2024) 10:509. doi: 10.3390/fermentation10100509 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

