Targeting inerleukin-6 for renoprotection
- PMID: 39723211
- PMCID: PMC11668664
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1502299
Targeting inerleukin-6 for renoprotection
Abstract
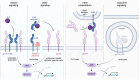
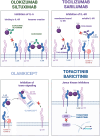
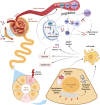
Sterile inflammation has been increasingly recognized as a hallmark of non-infectious kidney diseases. Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines in injured kidney tissue promotes infiltration of immune cells serving to clear cell debris and facilitate tissue repair. However, excessive or prolonged inflammatory response has been associated with immune-mediated tissue damage, nephron loss, and development of renal fibrosis. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a cytokine with pleiotropic effects including a major role in inflammation. IL-6 signals either via membrane-bound (classic signaling) or soluble receptor forms (trans-signaling) thus affecting distinct cell types and eliciting various metabolic, cytoprotective, or pro-inflammatory reactions. Antibodies neutralizing IL-6 or its receptor have been developed for therapy of autoimmune and chronic non-renal inflammatory diseases. Small molecule inhibitors of Janus kinases acting downstream of the IL-6 receptor, as well as recombinant soluble glycoprotein 130 variants suppressing the IL-6 trans-signaling add to the available therapeutic options. Animal data and accumulating clinical experience strongly suggest that suppression of IL-6 signaling pathways bears therapeutic potential in acute and chronic kidney diseases. The present work analyses the renoprotective potential of clinically relevant IL-6 signaling inhibitors in acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, and kidney transplantation with focus on current achievements and future prospects.
Keywords: IL-6; acute kidney injury; anti-cytokine therapy; chronic kidney disease; inflammation; kidney transplantation; trans-signaling.
Copyright © 2024 Gubernatorova, Samsonov, Drutskaya, Lebedeva, Bukhanova, Materenchuk and Mutig.
Conflict of interest statement
MS and DB are employed by R-Pharm JSC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

