Advances in biomarkers for immunotherapy in small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39723215
- PMCID: PMC11668642
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1490590
Advances in biomarkers for immunotherapy in small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
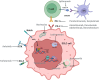
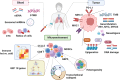
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a refractory cancer with rapid growth and high aggressiveness. Extensive-stage SCLC is initially sensitive to chemotherapy; however, drug resistance and recurrence occur rapidly, resulting in a poor survival outcome due to lack of subsequently efficient therapy. The emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) generated a new landscape of SCLC treatment and significantly prolonged the survival of patients. However, the unselected immunotherapy restrains both beneficiary population and responsive period in SCLC compared to the other tumors. The complex tumor origin, high heterogeneity, and immunosuppressive microenvironment may disturb the value of conventional biomarkers in SCLC including programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor mutation burden. Transcriptional regulator-based subtypes of SCLC are current research hotspot, revealing that Y (I) subtype can benefit from ICIs. Additionally, molecules related to immune microenvironment, immunogenicity, epigenetics, and SCLC itself also indicated the therapeutic benefits of ICIs, becoming potential predictive biomarkers. In this review, we discussed the advances of biomarkers for prediction and prognosis of immunotherapy, promising directions in the future, and provide reference and options for precision immunotherapy and survival improvement in patients with SCLC.
Keywords: biomarker; immunotherapy; predictive; prognosis; research advances; small-cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Zhao, Tian, Lu, Wang, Shao and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunotherapy for Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: Innovative Treatments and Future Perspectives.Cancer Control. 2025 Jan-Dec;32:10732748251334434. doi: 10.1177/10732748251334434. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Cancer Control. 2025. PMID: 40228829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Immunotherapy Advances in Small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020 Nov 20;23(11):989-998. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.105.02. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32752583 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Recent advances in immunotherapy for small cell lung cancer.Curr Opin Oncol. 2025 Jan 1;37(1):17-26. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000001105. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Curr Opin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39526685 Review.
-
Construction of a prognostic model for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer patients undergoing immune therapy in northernmost China and prediction of treatment efficacy based on response status at different time points.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 15;150(5):255. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05767-6. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38750370 Free PMC article.
-
[Expert consensus on immunotherapy for small cell lung cancer (2025 edition)].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2025 Jan 23;47(1):65-75. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20240905-00383. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39828584 Chinese.
Cited by
-
First-line serplulimab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Updated results and biomarker analysis from the ASTRUM-005 randomized clinical trial.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025 Aug;45(8):990-1009. doi: 10.1002/cac2.70032. Epub 2025 May 29. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40440184 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tracing the history of clinical practice of liquid biopsy: a bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 May 13;16:1574736. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1574736. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40433362 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Cancer Therapy: The Role of Personalized Medicine.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;17(5):725. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050725. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials