Paromomycin targets HDAC1-mediated SUMOylation and IGF1R translocation in glioblastoma
- PMID: 39723246
- PMCID: PMC11668589
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1490878
Paromomycin targets HDAC1-mediated SUMOylation and IGF1R translocation in glioblastoma
Abstract
Objective: This study investigates the effects of Paromomycin on SUMOylation-related pathways in glioblastoma (GBM), specifically targeting HDAC1 inhibition.
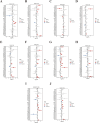
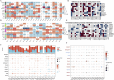
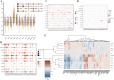
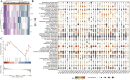
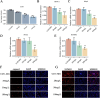
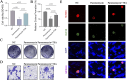
Methods: Using TCGA and GTEx datasets, we identified SUMOylation-related genes associated with GBM prognosis. Molecular docking analysis suggested Paromomycin as a potential HDAC1 inhibitor. In vitro assays on U-251MG GBM cells were performed to assess Paromomycin's effects on cell viability, SUMOylation gene expression, and IGF1R translocation using CCK8 assays, qRT-PCR, and immunofluorescence.
Results: Paromomycin treatment led to a dose-dependent reduction in GBM cell viability, colony formation, and migration. It modulated SUMO1 expression and decreased IGF1R nuclear translocation, an effect reversible by the HDAC1 inhibitor Trochostatin A (TSA), suggesting Paromomycin's involvement in SUMO1-regulated pathways.
Conclusion: This study highlights Paromomycin's potential as a therapeutic agent for GBM by targeting HDAC1-mediated SUMOylation pathways and influencing IGF1R translocation, warranting further investigation for its clinical application.
Keywords: HDAC1; IGF1R; Paromomycin; SUMOylation; drug screening; glioblastoma multiforme.
Copyright © 2024 Min, Guo and Ning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed M. G., Shaheen N., Shaheen A., Meshref M., Nashwan A. J., Nassar N. A., et al. (2024). Outcomes of endovascular treatment alone or with intravenous alteplase in acute ischemic stroke Patients: a retrospective cohort study. Brain Hemorrhages 5, 21–28. 10.1016/j.hest.2023.09.003 - DOI
-
- Aly A., Singh P., Korytowsky B., Ling Y.-L., Kale H. P., Dastani H. B., et al. (2019). Survival, costs, and health care resource use by line of therapy in US Medicare patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a retrospective observational study. Neuro-Oncology Pract. 7, 164–175. 10.1093/nop/npz042 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

