Bibliometric analysis of nanotechnology in spinal cord injury: current status and emerging frontiers
- PMID: 39723251
- PMCID: PMC11668783
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1473599
Bibliometric analysis of nanotechnology in spinal cord injury: current status and emerging frontiers
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to analyze the impact of nanotechnology on the treatment and recovery of spinal cord injury (SCI), a condition that has profound global effects on physical and psychological health.
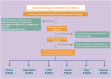
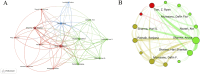
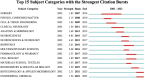
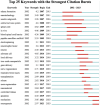
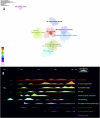
Methods: We utilized the Web of Science Core Collection to obtain bibliometric data. With the tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace, we conducted a comprehensive review of 422 relevant publications to identify research trends and influential works in the field of nanotechnology applied to SCI.
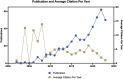
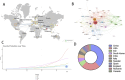
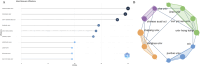
Results: The analysis revealed significant contributions from both China, Sweden and the United States, and pinpointed inflammation, apoptosis, and nano-drug delivery as the primary areas of focus in current research, with emerging trends evident in recent literature.
Conclusion: Nanotechnology hold great potential to revolutionize the treatment of SCI through targeted therapeutics and modulation of pathological processes. This study provided valuable insights into the evolving landscape of SCI research, underscoring the importance of continuous innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Keywords: CiteSpace; bibliometric; inflammation; nanotechnology; spinal cord injury.
Copyright © 2024 Gu, Zhang and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A bibliometric analysis of the research hotspots and frontiers related to cell death in spinal cord injury.Front Neurol. 2024 Jan 5;14:1280908. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1280908. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38249747 Free PMC article.
-
Global trends and emerging research in nanotechnology for esophageal cancer: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 3;16(1):262. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02018-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40029466 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Mapping of Macrophage in Spinal Cord Injury: A Bibliometric Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2023 Dec;180:e183-e197. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.09.022. Epub 2023 Sep 14. World Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 37714458
-
Bibliometric analysis of stem cells for spinal cord injury: current status and emerging frontiers.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 18;14:1235324. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1235324. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37533634 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis of spinal cord injury-associated macrophages from 2002 to 2023.Front Neurol. 2023 Nov 21;14:1285908. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1285908. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38073628 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

