NGF-mediated crosstalk: unraveling the influence of metabolic deregulation on the interplay between neural and pancreatic cancer cells and its impact on patient outcomes
- PMID: 39723256
- PMCID: PMC11668609
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1499414
NGF-mediated crosstalk: unraveling the influence of metabolic deregulation on the interplay between neural and pancreatic cancer cells and its impact on patient outcomes
Abstract
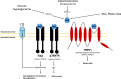
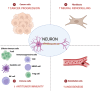
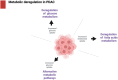
Neural invasion is one of the most common routes of invasion in pancreatic cancer and it is responsible for the high rate of tumor recurrence after surgery and the pain generation associated with pancreatic cancer. Several molecules implicated in neural invasion are also responsible for pain onset including NGF belonging to the family of neutrophins. NGF released by cancer cells can sensitize sensory nerves which in turn results in severe pain. NGF receptors, TrkA and P75NTR, are expressed on both PDAC cells and nerves, strongly suggesting their role in neural invasion. The crosstalk between the nervous system and cancer cells has emerged as an important regulator of pancreatic cancer and its microenvironment. Nerve cells influence the pancreatic tumor microenvironment and these interactions are important for cancer metabolism reprogramming and tumor progression. In this review, we summarized the current knowledge on the interaction between nerves and pancreatic cancer cells and its impact on cancer metabolism.
Keywords: NGF; metabolism; neural invasion; pain; pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Trentini, Agnetti, Manini, Giovannetti and Garajová.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bapat A. A., Hostetter G., Von Hoff D. D., Han H. (2011a). Perineural invasion and associated pain in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

